Page 381 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 381
Microeconomic Theory
Notes
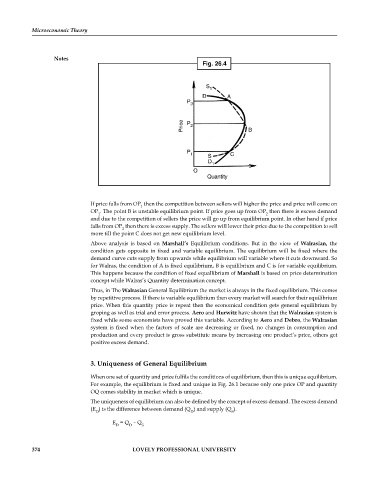
Fig. 26.4
S
1
D A
P
3
Price P 2 B
P
1 C
S
D
1
O
Quantity
If price falls from OP then the competition between sellers will higher the price and price will come on
1
OP . The point B is unstable equilibrium point. If price goes up from OP then there is excess demand
1
2
and due to the competition of sellers the price will go up from equilibrium point. In other hand if price
falls from OP then there is excess supply. The sellers will lower their price due to the competition to sell
2
more till the point C does not get new equilibrium level.
Above analysis is based on Marshall’s Equilibrium conditions. But in the view of Walrasian, the
condition gets opposite in fixed and variable equilibrium. The equilibrium will be fixed where the
demand curve cuts supply from upwards while equilibrium will variable where it cuts downward. So
for Walras, the condition of A is fixed equilibrium, B is equilibrium and C is for variable equilibrium.
This happens because the condition of fixed equallibrium of Marshall is based on price determination
concept while Walras’s Quantity determination concept.
Thus, in The Walrasian General Equilibrium the market is always in the fixed equilibrium. This comes
by repetitive process. If there is variable equilibrium then every market will search for their equilibrium
price. When this quantity price is repeat then the economical condition gets general equilibrium by
groping as well as trial and error process. Aero and Hurwitz have shown that the Walrasian system is
fixed while some economists have proved this variable. According to Aero and Debro, the Walrasian
system is fixed when the factors of scale are decreasing or fixed, no changes in consumption and
production and every product is gross substitute means by increasing one product’s price, others get
positive excess demand.
3. Uniqueness of General Equilibrium
When one set of quantity and price fulfils the conditions of equilibrium, then this is unique equilibrium.
For example, the equilibrium is fixed and unique in Fig. 26.1 because only one price OP and quantity
OQ comes stability in market which is unique.
The uniqueness of equilibrium can also be defined by the concept of excess demand. The excess demand
(E ) is the difference between demand (Q ) and supply (Q ).
S
D
D
E = Q – Q S
D
D
374 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY