Page 380 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 380
Unit-26: General Equilibrium Theory
Notes
Fig. 26.3
S
s D
P d
1
P E
d 1
P s
2 1
Price
O Q
Quantity
Self Assessment
Multiple choice questions:
4. When in a perfect competitive market, the difference factor does not found then there ....................
exists.
(a) general equilibrium (b) market equilibrium
(c) financial equilibrium (d) none of these
5. One equilibrium comes when demand and supply curve equals ................... .
(a) in a negative price (b) in a positive price
(c) in a general price (d) none of these
6. Walrasian General Equilibrium needs market equilibrium ................... .
(a) never (b) always
(c) no (d) none of these
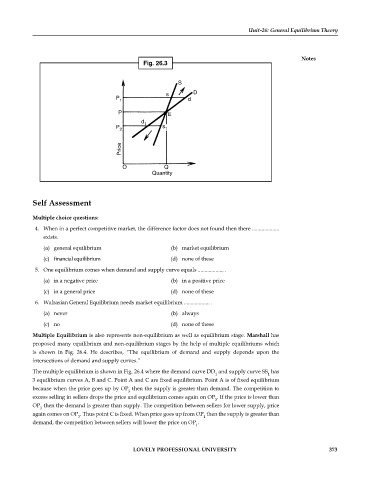
Multiple Equilibrium is also represents non-equilibrium as well as equilibrium stage. Marshall has
proposed many equilibrium and non-equilibrium stages by the help of multiple equilibriums which
is shown in Fig. 26.4. He describes, “The equilibrium of demand and supply depends upon the
intersections of demand and supply curves.”
The multiple equilibrium is shown in Fig. 26.4 where the demand curve DD and supply curve SS has
1 1
3 equilibrium curves A, B and C. Point A and C are fixed equilibrium. Point A is of fixed equilibrium
because when the price goes up by OP then the supply is greater than demand. The competition to
3
excess selling in sellers drops the price and equilibrium comes again on OP . If the price is lower than
3
OP then the demand is greater than supply. The competition between sellers for lower supply, price
3
again comes on OP . Thus point C is fixed. When price goes up from OP then the supply is greater than
1
3
demand, the competition between sellers will lower the price on OP .
1
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 373