Page 389 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 389
Microeconomic Theory
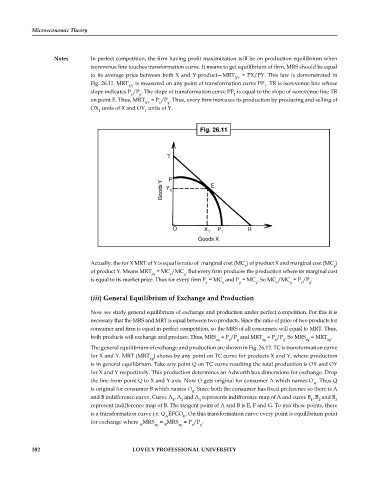
Notes In perfect competition, the firm having profit maximization will be on production equilibrium when
isorevenue line touches transformation curve. It means to get equilibrium of firm, MRS should be equal
to its average price between both X and Y product—MRT = PX/PY. This law is demonstrated in
XY
Fig. 26.11. MRT is measured on any point of transformation curve PP . TR is isorevenue line whose
XY 1
slope indicates P /P . The slope of transformation curve PP is equal to the slope of isorevenue line TR
x y 1
on point E. Thus, MRT = P /P . Thus, every firm increases its production by producing and selling of
y
x
XY
OX units of X and OY units of Y.
1 1
Fig. 26.11
T
P
Goods Y Y 1 E
O X P R
1 1
Goods X
Actually, the for X MRT of Y is equal is ratio of marginal cost (MC ) of product X and marginal cost (MC )
x y
of product Y. Means MRT = MC /MC . But every firm produces the production where its marginal cost
y
xy
x
is equal to its market price. Thus for every firm P = MC and P = MC . So MC /MC = P /P .
x x y y x y x y
(iii) General Equilibrium of Exchange and Production
Now we study general equilibrium of exchange and production under perfect competition. For this it is
necessary that the MRS and MRT is equal between two products. Since the ratio of price of two products for
consumer and firm is equal in perfect competition, so the MRS of all consumers will equal to MRT. Thus,
both products will exchange and produce. Thus, MRS = P /P and MRT = P /P . So MRS = MRT .
xy x y xy x y xy xy
The general equilibrium of exchange and production are shown in Fig. 26.12. TC is transformation curve
for X and Y. MRT (MRT ) shows by any point on TC curve for products X and Y, where production
xy
is in general equilibrium. Take any point Q on TC curve resulting the total production is OX and OY
for X and Y respectively. This production determines an Adworth box dimensions for exchange. Drop
the line from point Q to X and Y axis. Now O gets original for consumer A which names O . Thus Q
A
is original for consumer B which names O . Since both the consumer has fixed preference so there is A
B
and B indifference curve. Curve A , A and A represents indifference map of A and curve B , B and B
1
3
2
2
1
3
represent indifference map of B. The tangent point of A and B is E, F and G. To mix these points, there
is a transformation curve i.e. Q EFGO . On this transformation curve every point is equilibrium point
A B
for exchange where MRS = MRS = P /P .
A xy B xy x y
382 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY