Page 390 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 390
Unit-26: General Equilibrium Theory
Notes
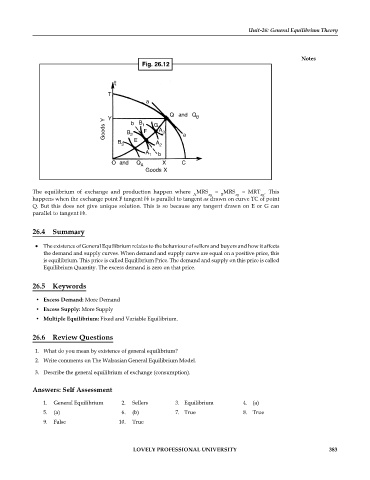
Fig. 26.12
t
T
a
Q and Q B
Y Y b B 1 G
Goods B 2 F A 3 a
B E A
3 2
A
1 b
O and Q X C
A
Goods X
The equilibrium of exchange and production happen where MRS = MRS = MRT . This
B
A
xy
xy
xy
happens when the exchange point F tangent bb is parallel to tangent aa drawn on curve TC of point
Q. But this does not give unique solution. This is so because any tangent drawn on E or G can
parallel to tangent bb.
26.4 Summary
• The existence of General Equilibrium relates to the behaviour of sellers and buyers and how it affects
the demand and supply curves. When demand and supply curve are equal on a positive price, this
is equilibrium. This price is called Equilibrium Price. The demand and supply on this price is called
Equilibrium Quantity. The excess demand is zero on that price.
26.5 Keywords
• Excess Demand: More Demand
• Excess Supply: More Supply
• Multiple Equilibrium: Fixed and Variable Equilibrium.
26.6 Review Questions
1. What do you mean by existence of general equilibrium?
2. Write comments on The Walrasian General Equilibrium Model.
3. Describe the general equilibrium of exchange (consumption).
Answers: Self Assessment
1. General Equilibrium 2. Sellers 3. Equilibrium 4. (a)
5. (a) 6. (b) 7. True 8. True
9. False 10. True
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 383