Page 55 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 55
Microeconomic Theory
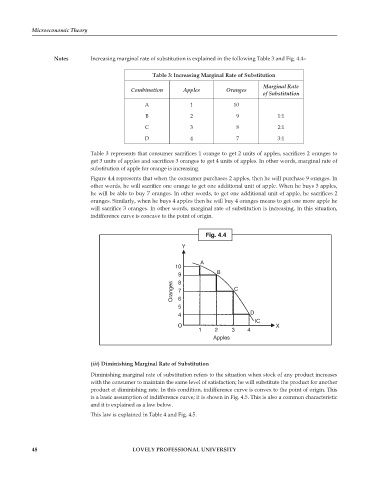
Notes Increasing marginal rate of substitution is explained in the following Table 3 and Fig. 4.4–
Table 3: Increasing Marginal Rate of Substitution
Marginal Rate
Combination Apples Oranges
of Substitution
A 1 10
B 2 9 1:1
C 3 8 2:1
D 4 7 3:1
Table 3 represents that consumer sacrifices 1 orange to get 2 units of apples, sacrifices 2 oranges to
get 3 units of apples and sacrifices 3 oranges to get 4 units of apples. In other words, marginal rate of
substitution of apple for orange is increasing.
Figure 4.4 represents that when the consumer purchases 2 apples, then he will purchase 9 oranges. In
other words, he will sacrifice one orange to get one additional unit of apple. When he buys 3 apples,
he will be able to buy 7 oranges. In other words, to get one additional unit of apple, he sacrifices 2
oranges. Similarly, when he buys 4 apples then he will buy 4 oranges means to get one more apple he
will sacrifice 3 oranges. In other words, marginal rate of substitution is increasing. In this situation,
indifference curve is concave to the point of origin.
Fig. 4.4
Y
A
10
9 B
8
Oranges 7 C
6
5
D
4
IC
O X
1 2 3 4
Apples
(iii) Diminishing Marginal Rate of Substitution
Diminishing marginal rate of substitution refers to the situation when stock of any product increases
with the consumer to maintain the same level of satisfaction; he will substitute the product for another
product at diminishing rate. In this condition, indifference curve is convex to the point of origin. This
is a basic assumption of indifference curve; it is shown in Fig. 4.5. This is also a common characteristic
and it is explained as a law below.
This law is explained in Table 4 and Fig. 4.5.
48 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY