Page 56 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 56
Unit-4: Ordinal Utility Theory: Indifference Curve Approach
Notes
Table 4: Diminishing Marginal Rate of Substitution
Marginal Rate
Combination Apples Oranges
of Substitution
A 1 10 —
B 2 7 3:1
C 3 5 2:1
D 4 4 1:1
Table 4 represents that the consumer will substitute 3 oranges for 2nd apple, 2 oranges for 3rd apple and
one orange for 4th apple means as he will take more number of apples, marginal rate of substitution of
apples for oranges will decrease.
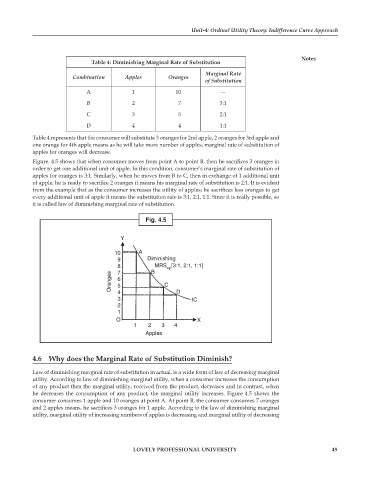
Figure. 4.5 shows that when consumer moves from point A to point B, then he sacrifices 3 oranges in
order to get one additional unit of apple. In this condition, consumer’s marginal rate of substitution of
apples for oranges is 3:1. Similarly, when he moves from B to C, then in exchange of 1 additional unit
of apple, he is ready to sacrifice 2 oranges it means his marginal rate of substitution is 2:1. It is evident
from the example that as the consumer increases the utility of apples; he sacrifices less oranges to get
every additional unit of apple it means the substitution rate is 3:1, 2:1, 1:1. Since it is really possible, so
it is called law of diminishing marginal rate of substitution.
Fig. 4.5
Y
10 A
9 Diminishing
8 B MRS [3:1, 2:1, 1:1]
xy
7
Oranges 6 C
5
4
3 D IC
2
1
O X
1 2 3 4
Apples
4.6 Why does the Marginal Rate of Substitution Diminish?
Law of diminishing marginal rate of substitution in actual, is a wide form of law of decreasing marginal
utility. According to law of diminishing marginal utility, when a consumer increases the consumption
of any product then the marginal utility, received from the product, decreases and in contrast, when
he decreases the consumption of any product, the marginal utility increases. Figure 4.5 shows the
consumer consumes 1 apple and 10 oranges at point A. At point B, the consumer consumes 7 oranges
and 2 apples means, he sacrifices 3 oranges for 1 apple. According to the law of diminishing marginal
utility, marginal utility of increasing numbers of apples is decreasing and marginal utility of decreasing
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 49