Page 60 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 60
Unit-4: Ordinal Utility Theory: Indifference Curve Approach
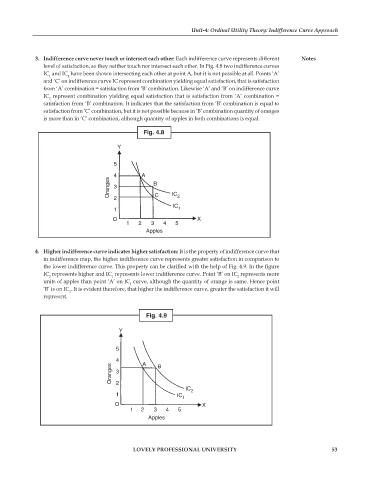
3. Indifference curve never touch or intersect each other: Each indifference curve represents different Notes
level of satisfaction, so they neither touch nor intersect each other. In Fig. 4.8 two indifference curves
IC and IC have been shown intersecting each other at point A, but it is not possible at all. Points ‘A’
1
2
and ‘C’ on indifference curve IC represent combination yielding equal satisfaction, that is satisfaction
from ‘A’ combination = satisfaction from ‘B’ combination. Likewise ‘A’ and ‘B’ on indifference curve
IC represent combination yielding equal satisfaction that is satisfaction from ‘A’ combination =
2
satisfaction from ‘B’ combination. It indicates that the satisfaction from ‘B’ combination is equal to
satisfaction from ‘C’ combination, but it is not possible because in ‘B’ combination quantity of oranges
is more than in ‘C’ combination, although quantity of apples in both combinations is equal.
Fig. 4.8
Y
5
4 A
Oranges 3 B C IC 2
2
IC
1 1
O X
1 2 3 4 5
Apples
4. Higher indifference curve indicates higher satisfaction: It is the property of indifference curve that
in indifference map, the higher indifference curve represents greater satisfaction in comparison to
the lower indifference curve. This property can be clarified with the help of Fig. 4.9. In the figure
IC represents higher and IC represents lower indifference curve. Point ‘B’ on IC represents more
2
2
1
units of apples than point ‘A’ on IC curve, although the quantity of orange is same. Hence point
1
‘B’ is on IC . It is evident therefore, that higher the indifference curve, greater the satisfaction it will
1
represent.
Fig. 4.9
Y
5
4 A B
Oranges 3
2
IC 2
1 IC
1
O X
1 2 3 4 5
Apples
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 53