Page 64 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 64
Unit-4: Ordinal Utility Theory: Indifference Curve Approach
According to Hibbdon, “The budget line is that line which shows all the different combinations Notes
of two commodities that a consumer can purchase, give his money, income and the price of two
commodities.”
Explanation
Suppose income of the consumer is 4.00, he wishes to spend all his money on apples and oranges.
Price of oranges is 0.50 per orange and price of apple is 1.00 per apple. Combinations of these two
commodities which the consumer can buy with his definite income and definite price of apples and
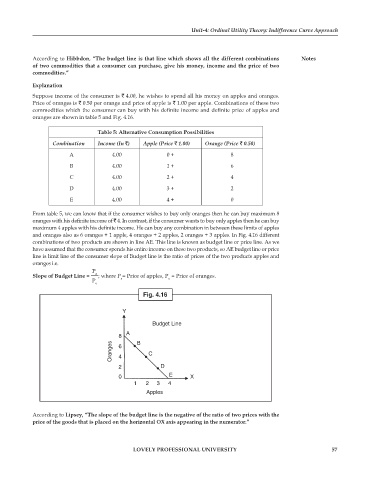
oranges are shown in table 5 and Fig. 4.16.
Table 5: Alternative Consumption Possibilities
Combination Income (In ) Apple (Price 1.00) Orange (Price 0.50)
A 4.00 0 + 8
B 4.00 1 + 6
C 4.00 2 + 4
D 4.00 3 + 2
E 4.00 4 + 0
From table 5, we can know that if the consumer wishes to buy only oranges then he can buy maximum 8
oranges with his definite income of 4. In contrast, if the consumer wants to buy only apples then he can buy
maximum 4 apples with his definite income. He can buy any combination in between these limits of apples
and oranges also as 6 oranges + 1 apple, 4 oranges + 2 apples, 2 oranges + 3 apples. In Fig. 4.16 different
combinations of two products are shown in line AE. This line is known as budget line or price line. As we
have assumed that the consumer spends his entire income on these two products, so AE budget line or price
line is limit line of the consumer slope of Budget line is the ratio of prices of the two products apples and
oranges i.e.
P
Slope of Budget Line = a ; where P = Price of apples, P = Price of oranges.
P o a o
Fig. 4.16
Y
Budget Line
A
8 B
Oranges 6 C
4
2 D
0 E X
1 2 3 4
Apples
According to Lipsey, “The slope of the budget line is the negative of the ratio of two prices with the
price of the goods that is placed on the horizontal OX axis appearing in the numerator.”
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 57