Page 69 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 69
Microeconomic Theory
Notes has not defined the maximum satisfaction on given curve. Actually, the tangent point E would be the
lowest satisfaction point on lowermost indifference curve, while the uppermost marginal curve would
be in a point of budget line (as R point is shown on diagram). To move left or right on budget line AB,
can touch the indifference curve until consumer not touches the point R on indifference curve IC . This
2
point represents the status of corner equilibrium. In other words, if indifference curve is concave then
the equilibrium state will be at the end which represents that only one product is used. The consumer
only buys apples not oranges in the corner equilibrium point E. So the consumer will get maximum
satisfaction when indifference curve touches not only the budget line but also upward on the root point.
4.16 Effect of Change in Commodity Price on Consumer’s Equilibrium
The effect of a product price due to its demanded quantity is called Price Effect. It can be classified into
two parts (i) Income Effect and (ii) Substitution Effect.
Price Effect = Income Effect and Substitution Effect
4.17 Price Effect
The price effect may be defined as the change in the consumption of goods, when the price of either
of the two goods changes while the price of the other goods and the income of the consumer remain
constant.
In the words of Richards G. Lipsey, “The price effect shows how much satisfaction of the consumer
varies due to change in the consumption of two goods as the price of one changes, the price of the other
and money income remains constant.”
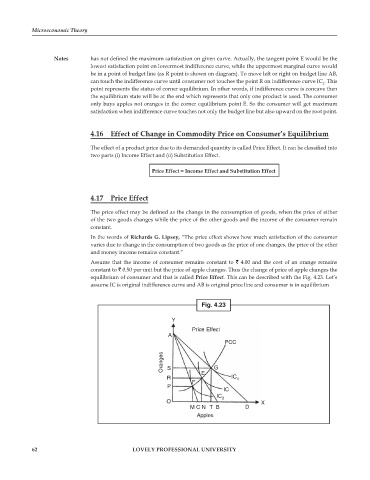
Assume that the income of consumer remains constant to 4.00 and the cost of an orange remains
constant to 0.50 per unit but the price of apple changes. Thus the change of price of apple changes the
equilibrium of consumer and that is called Price Effect. This can be described with the Fig. 4.23. Let’s
assume IC is original indifference curve and AB is original price line and consumer is in equilibrium
Fig. 4.23
Y
Price Effect
A
PCC
Oranges S G
E
R IC 1
F
P
IC
IC 2
O X
M C NT B D
Apples
62 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY