Page 66 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 66
Unit-4: Ordinal Utility Theory: Indifference Curve Approach
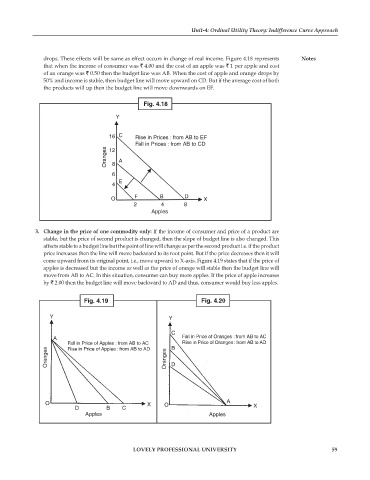
drops. These effects will be same as effect occurs in change of real income. Figure 4.18 represents Notes
that when the income of consumer was 4.00 and the cost of an apple was 1 per apple and cost
of an orange was 0.50 then the budget line was AB. When the cost of apple and orange drops by
50% and income is stable, then budget line will move upward on CD. But if the average cost of both
the products will up then the budget line will move downwards on EF.
Fig. 4.18
Y
16 C Rise in Prices : from AB to EF
Fall in Prices : from AB to CD
Oranges 12 A
8
6
E
4
O F B D X
2 4 8
Apples
3. Change in the price of one commodity only: If the income of consumer and price of a product are
stable, but the price of second product is changed, then the slope of budget line is also changed. This
affects stable to a budget line but the point of line will change as per the second product i.e. if the product
price increases then the line will move backward to its root point. But if the price decreases then it will
come upward from its original point, i.e., move upward to X-axis. Figure 4.19 states that if the price of
apples is decreased but the income as well as the price of orange will stable then the budget line will
move from AB to AC. In this situation, consumer can buy more apples. If the price of apple increases
by 2.00 then the budget line will move backward to AD and thus, consumer would buy less apples.
Fig. 4.19 Fig. 4.20
Y Y
C
A Fall in Price of Oranges : from AB to AC
Fall in Price of Apples : from AB to AC B Rise in Price of Oranges : from AB to AD
Oranges Oranges D
Rise in Price of Apples : from AB to AD
O X O A
D B C X
Apples Apples
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 59