Page 91 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 91
Microeconomic Theory
Notes Under this theory, a consumer will buy a combination of two products because either he likes this
rather than other combinations or it is cheaper than others. Suppose that a consumer buys combination
A rather than B, C or D combination. This is because he reveals preferences towards A. This can be
done due to two reasons. First that the combination of A is cheaper than combinations of B, C or D;
or the consumer really likes combination A from other combinations even it is costlier than others. In
this situation, it can be said that A has revealed preferences than B, C and D or B, C and D are revealed
inferior than A.
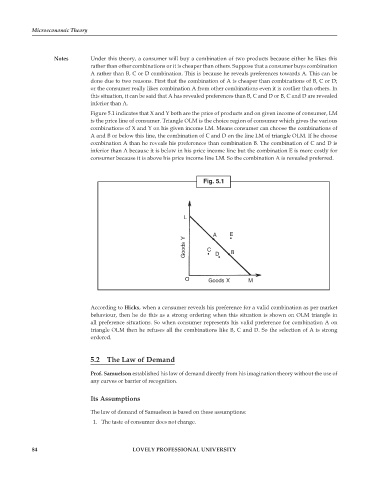
Figure 5.1 indicates that X and Y both are the price of products and on given income of consumer, LM
is the price line of consumer. Triangle OLM is the choice region of consumer which gives the various
combinations of X and Y on his given income LM. Means consumer can choose the combinations of
A and B or below this line, the combination of C and D on the line LM of triangle OLM. If he choose
combination A than he reveals his preferences than combination B. The combination of C and D is
inferior than A because it is below in his price income line but the combination E is more costly for
consumer because it is above his price income line LM. So the combination A is revealed preferred.
Fig. 5.1
L
A E
Goods Y C D B
O Goods X M
According to Hicks, when a consumer reveals his preference for a valid combination as per market
behaviour, then he do this as a strong ordering when this situation is shown on OLM triangle in
all preference situations. So when consumer represents his valid preference for combination A on
triangle OLM then he refuses all the combinations like B, C and D. So the selection of A is strong
ordered.
5.2 The Law of Demand
Prof. Samuelson established his law of demand directly from his imagination theory without the use of
any curves or barrier of recognition.
Its Assumptions
The law of demand of Samuelson is based on these assumptions:
1. The taste of consumer does not change.
84 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY