Page 95 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 95
Microeconomic Theory
Notes
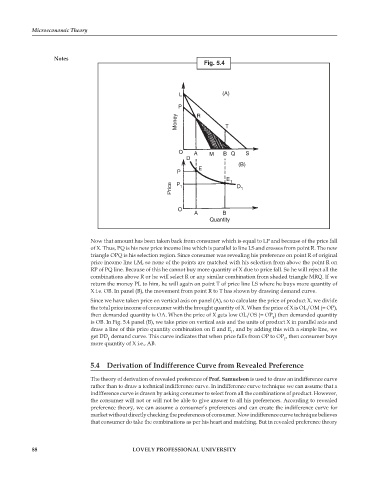
Fig. 5.4
L (A)
P
Money R T
O A M B Q S
D
(B)
E
P
E 1
Price P 1 D 1
O
A B
Quantity
Now that amount has been taken back from consumer which is equal to LP and because of the price fall
of X. Thus, PQ is his new price income line which is parallel to line LS and crosses from point R. The new
triangle OPQ is his selection region. Since consumer was revealing his preference on point R of original
price income line LM, so none of the points are matched with his selection from above the point R on
RP of PQ line. Because of this he cannot buy more quantity of X due to price fall. So he will reject all the
combinations above R or he will select R or any similar combination from shaded triangle MRQ. If we
return the money PL to him, he will again on point T of price line LS where he buys more quantity of
X i.e. OB. In panel (B), the movement from point R to T has shown by drawing demand curve.
Since we have taken price on vertical axis on panel (A), so to calculate the price of product X, we divide
the total price income of consumer with the brought quantity of X. When the price of X is OL/OM (= OP),
then demanded quantity is OA. When the price of X gets low OL/OS (= OP ) then demanded quantity
1
is OB. In Fig. 5.4 panel (B), we take price on vertical axis and the units of product X in parallel axis and
draw a line of this price quantity combination on E and E , and by adding this with a simple line, we
1
get DD demand curve. This curve indicates that when price falls from OP to OP , then consumer buys
1
1
more quantity of X i.e., AB.
5.4 Derivation of Indifference Curve from Revealed Preference
The theory of derivation of revealed preference of Prof. Samuelson is used to draw an indifference curve
rather than to draw a technical indifference curve. In indifference curve technique we can assume that a
indifference curve is drawn by asking consumer to select from all the combinations of product. However,
the consumer will not or will not be able to give answer to all his preferences. According to revealed
preference theory, we can assume a consumer’s preferences and can create the indifference curve for
market without directly checking the preferences of consumer. Now indifference curve technique believes
that consumer do take the combinations as per his heart and matching. But in revealed preference theory
88 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY