Page 97 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 97
Microeconomic Theory
Notes All the points would not match with him on the left side of B on this line KB. Since consumer selects
combination B, it looks like more inferior to R and all the points above and below of BN look inferior.
Thus, triangle BNM has been cut by below ignorance region. To draw these types of budget line in point
R and by giving this type of fact, all the portions can be removed from the below ignorance region R.
Thus, we can cut the left side of R on above ignorance region in Fig. 5.6. Suppose that the price of X
increases and the new budget line PQ crosses the original point R, which indicates that real income is
on point R. Now consumer selects a new point A on budget line PQ. Thus he reveals preference for A
rather than R, because both the points are on a single budget line. But A gets preference on the right
side of A and the above GAH region. Because this region represents those combinations on which a
product’s quantity is greater than the product combinations of A. This can be understand as because
A is preferable to R and GAH region is preferable to A, so GAH is preferable to R. Thus in GAHT
region by ranking the combinations and giving preference to R, we remove some of the upper parts
or ignorance region. To duplicate this process, we do lessen the ignorance region and established the
indifference region, which is shown by I curve in Fig. 5.7.
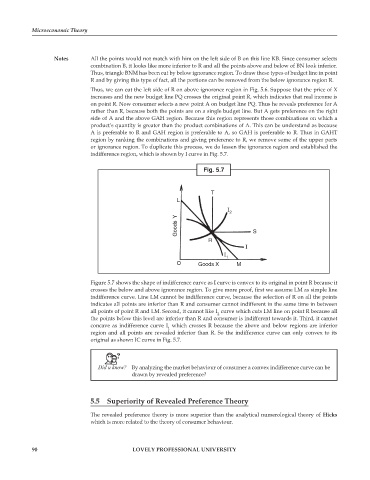
Fig. 5.7
T
L
I
2
Goods Y S
R
I
I
1
O Goods X M
Figure 5.7 shows the shape of indifference curve as I curve is convex to its original in point R because it
crosses the below and above ignorance region. To give more proof, first we assume LM as simple line
indifference curve. Line LM cannot be indifference curve, because the selection of R on all the points
indicates all points are inferior than R and consumer cannot indifferent in the same time in between
all points of point R and LM. Second, it cannot like I curve which cuts LM line on point R because all
2
the points below this level are inferior than R and consumer is indifferent towards it. Third, it cannot
concave as indifference curve I which crosses R because the above and below regions are inferior
1
region and all points are revealed inferior than R. So the indifference curve can only convex to its
original as shown IC curve in Fig. 5.7.
By analyzing the market behaviour of consumer a convex indifference curve can be
drawn by revealed preference?
5.5 Superiority of Revealed Preference Theory
The revealed preference theory is more superior than the analytical numerological theory of Hicks
which is more related to the theory of consumer behaviour.
90 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY