Page 160 - DECO402_Macro Economics
P. 160
Unit-17: Money Multiplier and Credit Creation by Commercial Banks
as much less will the cash reserve ratio be that much more will the creation of credit be. For Notes
example,
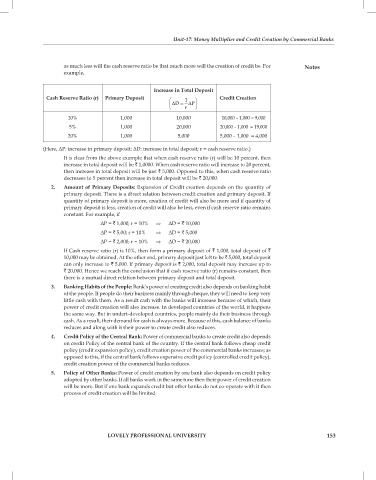
Increase in Total Deposit
Cash Reserve Ratio (r) Primary Deposit 1 Credit Creation
∆ D = ∆ P
r
10% 1,000 10,000 10,000 – 1,000 = 9,000
5% 1,000 20,000 20,000 – 1,000 = 19,000
20% 1,000 5,000 5,000 – 1,000 = 4,000
(Here, ΔP: increase in primary deposit; ΔD: increase in total deposit; r = cash reserve ratio.)
It is clear from the above example that when cash reserve ratio (r) will be 10 percent, then
increase in total deposit will be ` 1,0000. When cash reserve ratio will increase to 20 percent,
then increase in total deposit will be just ` 5,000. Opposed to this, when cash reserve ratio
decreases to 5 percent then increase in total deposit will be ` 20,000.
2. Amount of Primary Deposits: Expansion of Credit creation depends on the quantity of
primary deposit. There is a direct relation between credit creation and primary deposit. If
quantity of primary deposit is more, creation of credit will also be more and if quantity of
primary deposit is less, creation of credit will also be less, even if cash reserve ratio remains
constant. For example, if
ΔP = ` 1,000; r = 10% ⇒ ΔD = ` 10,000
ΔP = ` 5,00; r = 10% ⇒ ΔD = ` 5,000
ΔP = ` 2,000; r = 10% ⇒ ΔD = ` 20,000
If Cash reserve ratio (r) is 10%, then form a primary deposit of ` 1,000, total deposit of `
10,000 may be obtained. At the other end, primary deposit just left to be ` 5,000, total deposit
can only increase to ` 5,000. If primary deposit is ` 2,000, total deposit may increase up to
` 20,000. Hence we reach the conclusion that if cash reserve ratio (r) remains constant, then
there is a mutual direct relation between primary deposit and total deposit.
3. Banking Habits of the People: Bank’s power of creating credit also depends on banking habit
of the people. If people do their business mainly through cheque, they will need to keep very
little cash with them. As a result cash with the banks will increase because of which, their
power of credit creation will also increase. In developed countries of the world, it happens
the same way. But in undert-developed countries, people mainly do their business through
cash. As a result, their demand for cash is always more. Because of this, cash balance of banks
reduces and along with it their power to create credit also reduces.
4. Credit Policy of the Central Bank: Power of commercial banks to create credit also depends
on credit Policy of the central bank of the country. If the central bank follows cheap credit
policy (credit expansion policy), credit creation power of the commercial banks increases; as
opposed to this, if the central bank follows expensive credit policy (controlled credit policy),
credit creation power of the commercial banks reduces.
5. Policy of Other Banks: Power of credit creation by one bank also depends on credit policy
adopted by other banks. If all banks work in the same tune then their power of credit creation
will be more. But if one bank expands credit but other banks do not co-operate with it then
process of credit creation will be limited.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 153