Page 175 - DECO503_INTERNATIONAL_TRADE_AND_FINANCE_ENGLISH
P. 175
Unit 14 : Exchange Rate : Meaning and Components
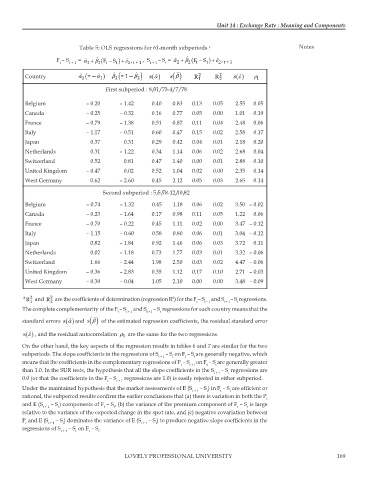
Table 5: OLS regressions for 61-month subperiods. a Notes
ˆ
ˆ
F – S t + 1 = ˆ α + β 1 ( t S + ε 1 t + 1 , S t + 1 – S = ˆ α + β 2 ( t S + ε 2 t + 1
F −
ˆ ,
F −
ˆ ,
) t
2
1
t
) t
t
( )
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
Country ˆ α 2 (=—α 1 ) β 2 ( =1—β 2 ) s ( ) ˆ α s β R 2 1 R 2 2 s () ˆ ε ρ 1
First subperiod : 8/31/ 73-4/ 7/ 78
Belgium – 0.20 – 1.42 0.40 0.83 0.13 0.05 2.55 0.05
Canada – 0.25 – 0.32 0.16 0.77 0.05 0.00 1.01 0.19
France – 0.79 – 1.38 0.51 0.87 0.11 0.04 2.48 0.06
Italy – 1.17 – 0.51 0.60 0.47 0.15 0.02 2.58 0.17
Japan 0.37 0.31 0.29 0.42 0.04 0.01 2.18 0.20
Netherlands 0.31 – 1.22 0.34 1.14 0.06 0.02 2.68 0.04
Switzerland 0.52 0.81 0.47 1.40 0.00 0.01 2.88 0.10
United Kingdom – 0.47 0.02 0.52 1.04 0.02 0.00 2.35 0.14
West Germany 0.62 – 2.60 0.45 2.12 0.05 0.03 2.65 0.14
Second subperiod : 5/5/78-12/10/82
Belgium – 0.74 – 1.32 0.45 1.18 0.06 0.02 3.50 – 0.02
Canada – 0.23 – 1.64 0.17 0.98 0.11 0.05 1.22 0.06
France – 0.70 – 0.22 0.45 1.11 0.02 0.00 3.47 – 0.12
Italy – 1.15 – 0.60 0.58 0.80 0.06 0.01 3.04 – 0.12
Japan 0.82 – 1.84 0.92 1.46 0.06 0.03 3.72 0.11
Netherlands 0.02 – 1.18 0.73 1.77 0.03 0.01 3.32 – 0.06
Switzerland 1.66 – 2.44 1.98 2.50 0.03 0.02 4.47 – 0.06
United Kingdom – 0.36 – 2.83 0.35 1.12 0.17 0.10 2.71 – 0.03
West Germany – 0.30 – 0.04 1.05 2.10 0.00 0.00 3.48 – 0.09
a R and R are the coefficients of determination (regression R ) for the F – S t – 1 and S t + 1 – S regressions.
2
2
2
2
1
t
t
The complete complementarity of the F – S and S – S regressions for each country means that the
t t + 1 t + 1 t
ˆ
β
α
s
s
standard errors () ˆ and ( ) of the estimated regression coefficients, the residual standard error
s () ε ˆ , and the residual autocorrelation ρ are the same for the two regressions.
1
On the other hand, the key aspects of the regression results in tables 6 and 7 are similar for the two
subperiods. The slope coefficients in the regressions of S – S on F – S are generally negative, which
t + 1 t t t
means that the coefficients in the complementary regressions of F – S on F – S are generally greater
t t + 1 t t
than 1.0. In the SUR tests, the hypothesis that all the slope coefficients in the S – S regressions are
t + 1 t
0.0 (or that the coefficients in the F – S regressions are 1.0) is easily rejected in either subperiod.
t t + 1
Under the maintained hypothesis that the market assessments of E (S – S ) in F – S are efficient or
t + 1 t t t
rational, the subperiod results confirm the earlier conclusions that (a) there is variation in both the P
t
and E (S – S ) components of F – S , (b) the variance of the premium component of F – S is large
t + 1 t t t t t
relative to the variance of the expected change in the spot rate, and (c) negative covariation between
P and E (S – S ) dominates the variance of E (S – S ) to produce negative slope coefficients in the
t t + 1 t t + 1 t
regressions of S – S on F – S .
t + 1 t t t
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 169