Page 223 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 223
Unit 16: Methods—Simple (Unweighted) Aggregate Method and Weighted Aggregate Method
16.1 Simple (Unweighted) Aggregate Method Notes
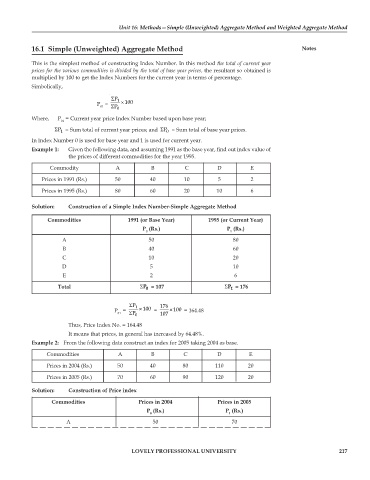
This is the simplest method of constructing Index Number. In this method the total of current year
prices for the various commodities is divided by the total of base year prices, the resultant so obtained is
multiplied by 100 to get the Index Numbers for the current year in terms of percentage.
Simbolically,
ΣP 1
P = × 100
01 ΣP 0
Where, P = Current year price Index Number based upon base year;
01
ΣP = Sum total of current year prices; and ΣP = Sum total of base year prices.
0
1
In Index Number 0 is used for base year and 1 is used for current year.
Example 1: Given the following data, and assuming 1991 as the base year, find out index value of
the prices of different commodities for the year 1995.
Commodity A B C D E
Prices in 1991 (Rs.) 50 40 10 5 2
Prices in 1995 (Rs.) 80 60 20 10 6
Solution: Construction of a Simple Index Number-Simple Aggregate Method
Commodities 1991 (or Base Year) 1995 (or Current Year)
P (Rs.) P (Rs.)
0 1
A 50 80
B 40 60
C 10 20
D 5 10
E 2 6
Total Σ P = 107 Σ P = 176
0
1
ΣP 1 176
P = × 100 = × 100 = 164.48
01 ΣP 0 107
Thus, Price Index No. = 164.48
It means that prices, in general has increased by 64.48%.
Example 2: From the following data construct an index for 2005 taking 2004 as base.
Commodities A B C D E
Prices in 2004 (Rs.) 50 40 80 110 20
Prices in 2005 (Rs.) 70 60 90 120 20
Solution: Construction of Price index
Commodities Prices in 2004 Prices in 2005
P (Rs.) P (Rs.)
0 1
A 50 70
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 217