Page 228 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 228
Statistical Methods in Economics
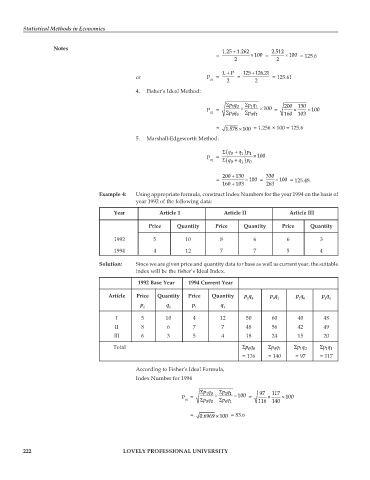
Notes 1.25 1.262 2.512
+
= × 100 = × 100 = 125.6
2 2
+
+
LP 125 126.21
or P = = = 125.61
01 2 2
4. Fisher’s Ideal Method:
Σ 10 Σpq pq 200 130
1 1
P = × × 100 = × × 100
01 Σ 00 Σpq pq 160 103
01
= 1.578 100× = 1.256 × 100 = 125.6
5. Marshall-Edgeworth Method:
Σ ( q + q 1 ) 0 p 1
P = × 100
01 Σ ( q + q 1 ) 0 p 0
+
200 130 330
= × 100 = × 100 = 125.48.
+
160 103 263
Example 4: Using appropriate formula, construct Index Numbers for the year 1994 on the basis of
year 1992 of the following data:
Year Article 1 Article II Article III
Price Quantity Price Quantity Price Quantity
1992 5 10 8 6 6 3
1994 4 12 7 7 5 4
Solution: Since we are given price and quantity data for base as well as current year, the suitable
index will be the fisher’s Ideal Index.
1992 Base Year 1994 Current Year
Article Price Quantity Price Quantity p q p q p q p q
0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
p q p q
0 0 1 1
I 5 10 4 12 50 60 40 48
II 8 6 7 7 48 56 42 49
III 6 3 5 4 18 24 15 20
Total Σpq Σpq Σpq Σpq
00
10
11
01
= 116 = 140 = 97 = 117
According to Fisher’s Ideal Formula,
Index Number for 1994
Σ Σpq pq 97 117
P = 10 × 1 1 × 100 = × × 100
01 Σ 00 Σpq pq 116 140
01
= 0.6969 100 = 83.6
×
222 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY