Page 229 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 229
Unit 16: Methods—Simple (Unweighted) Aggregate Method and Weighted Aggregate Method
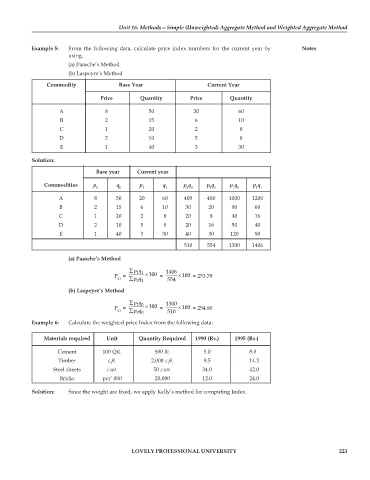
Example 5: From the following data, calculate price index numbers for the current year by Notes
using.
(a) Paasche’s Method
(b) Laspeyre’s Method
Commodity Base Year Current Year
Price Quantity Price Quantity
A 8 50 20 60
B 2 15 6 10
C 1 20 2 8
D 2 10 5 8
E 1 40 3 30
Solution:
Base year Current year
Commodities p q p q p q p q p q p q
0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
A 8 50 20 60 400 480 1000 1200
B 2 15 6 10 30 20 90 60
C 1 20 2 8 20 8 40 16
D 2 10 5 8 20 16 50 40
E 1 40 3 30 40 30 120 90
510 554 1300 1406
(a) Paasche’s Method
∑ pq 1406
11
P = × 100 = × 100 = 253.79
01 ∑ pq 554
01
(b) Laspeyre’s Method
∑ pq 1300
P = 10 × 100 = × 100 = 254.90
01 ∑ pq 510
00
Example 6: Calculate the weighted price Index from the following data:
Materials required Unit Quantity Required 1990 (Rs.) 1995 (Rs.)
Cement 100 Qtl. 500 lb. 5.0 8.0
Timber c.ft. 2,000 c.ft. 9.5 14.2
Steel sheets c.wt. 50 c.wt. 34.0 42.0
Bricks per’ 000 20,000 12.0 24.0
Solution: Since the weight are fixed, we apply Kelly’s method for computing Index.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 223