Page 227 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 227
Unit 16: Methods—Simple (Unweighted) Aggregate Method and Weighted Aggregate Method
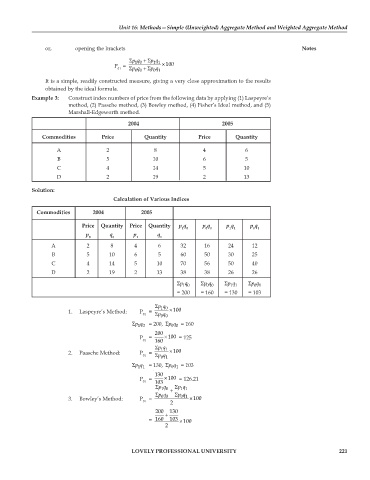
or, opening the brackets Notes
Σ 10 +pq Σ p q
11
P = ×100
01 Σ 00 +pq Σ pq
0 1
It is a simple, readily constructed measure, giving a very close approximation to the results
obtained by the ideal formula.
Example 3: Construct index numbers of price from the following data by applying (1) Laspeyre’s
method, (2) Passche method, (3) Bowley method, (4) Fisher’s Ideal method, and (5)
Marshall-Edgeworth method.
2004 2005
Commodities Price Quantity Price Quantity
A 2 8 4 6
B 5 10 6 5
C 4 14 5 10
D 2 19 2 13
Solution:
Calculation of Various Indices
Commodities 2004 2005
Price Quantity Price Quantity p q p q p q p q
1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1
p q p q
0 0 1 1
A 2 8 4 6 32 16 24 12
B 5 10 6 5 60 50 30 25
C 4 14 5 10 70 56 50 40
D 2 19 2 13 38 38 26 26
Σpq Σpq Σpq Σpq
10
01
00
11
= 200 = 160 = 130 = 103
Σpq
10
1. Laspeyre’s Method: P = ×100
01 Σpq
00
Σpq = 200, Σpq = 160
00
10
200
P = × 100 = 125
01 160
Σpq
11
2. Paasche Method: P = ×100
01 Σpq
01
Σpq 01
11 = 130, Σpq = 103
130
P = × 100 = 126.21
01 103
Σ 10 + Σpq p q
1 1
Σ Σpq pq
3. Bowley’s Method: P = 00 0 1 ×100
01 2
200 + 130
= 160 103 × 100
2
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 221