Page 237 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 237
Unit 17: Methods: Simple (Unweighted) Aggregate Method
Merits and Demerits of Simple Aggregate Method: Simple aggregative method of index number Notes
construction is very easy but it can be applied only when the prices of all commodities have been
expressed in the same unit. If units are different, the retults will be misleading?
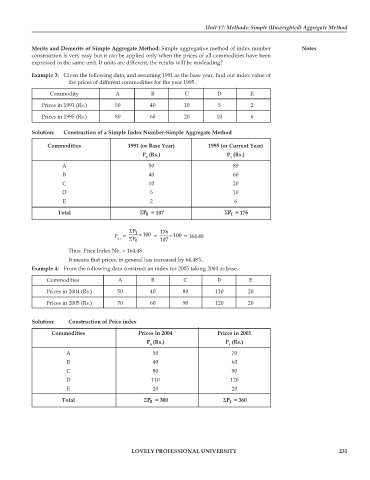
Example 3: Given the following data, and assuming 1991 as the base year, find out index value of
the prices of different commodities for the year 1995.
Commodity A B C D E
Prices in 1991 (Rs.) 50 40 10 5 2
Prices in 1995 (Rs.) 80 60 20 10 6
Solution: Construction of a Simple Index Number-Simple Aggregate Method
Commodities 1991 (or Base Year) 1995 (or Current Year)
P (Rs.) P (Rs.)
0 1
A 50 80
B 40 60
C 10 20
D 5 10
E 2 6
Total Σ P 0 = 107 Σ P 1 = 176
ΣP 1 176
P = × 100 = × 100 = 164.48
01 ΣP 0 107
Thus, Price Index No. = 164.48
It means that prices, in general has increased by 64.48%.
Example 4: From the following data construct an index for 2005 taking 2004 as base.
Commodities A B C D E
Prices in 2004 (Rs.) 50 40 80 110 20
Prices in 2005 (Rs.) 70 60 90 120 20
Solution: Construction of Price index
Commodities Prices in 2004 Prices in 2005
P (Rs.) P (Rs.)
0 1
A 50 70
B 40 60
C 80 90
D 110 120
E 20 20
Total Σ P = 300 Σ P = 360
0
1
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 231