Page 25 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 25
Unit 3: Classification and Tabulation of Data: Frequency and Cumulative Frequency Distribution
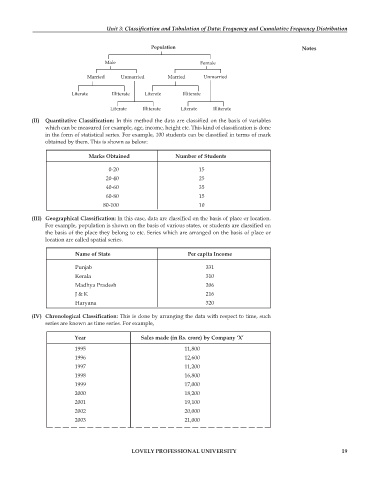
Population Notes
Male Female
Married Unmarried Married Unmarried
Literate Illiterate Literate Illiterate
Literate Illiterate Literate Illiterate
(II) Quantitative Classification: In this method the data are classified on the basis of variables
which can be measured for example, age, income, height etc. This kind of classification is done
in the form of statistical series. For example, 100 students can be classified in terms of mark
obtained by them. This is shown as below:
Marks Obtained Number of Students
0-20 15
20-40 25
40-60 35
60-80 15
80-100 10
(III) Geographical Classification: In this case, data are classified on the basis of place or location.
For example, population is shown on the basis of various states, or students are classified on
the basis of the place they belong to etc. Series which are arranged on the basis of place or
location are called spatial series.
Name of State Per capita Income
Punjab 331
Kerala 310
Madhya Pradesh 206
J & K 216
Haryana 320
(IV) Chronological Classification: This is done by arranging the data with respect to time, such
series are known as time series. For example,
Year Sales made (in Rs. crore) by Company ‘X’
1995 11,800
1996 12,600
1997 11,200
1998 16,800
1999 17,000
2000 18,200
2001 19,100
2002 20,000
2003 21,000
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 19