Page 29 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 29
Unit 3: Classification and Tabulation of Data: Frequency and Cumulative Frequency Distribution
(7) ‘Zero’ quantity must be indicated separately, and in case of unavailability of a particular Notes
figure ‘NA’ (not available) must be indicated clearly. ‘Zero’ is not equivalent to ‘Not
available’.
(8) Abbreviations should be avoided. But if the need so arises, it must be clarified in footnotes.
(9) The tabulation should be explicit. Words like ‘etc’. must not be used.
(10) The table should be of manageable size.
Tabulation is an art which requires common sense in planning a table and viewing the
proposed table from the point of view of the user or the other person. Tabulation is done
keeping in mind the purpose of statistical investigation. The rules of tabulation act as
guides in preparing a good table.
Seriations of Data
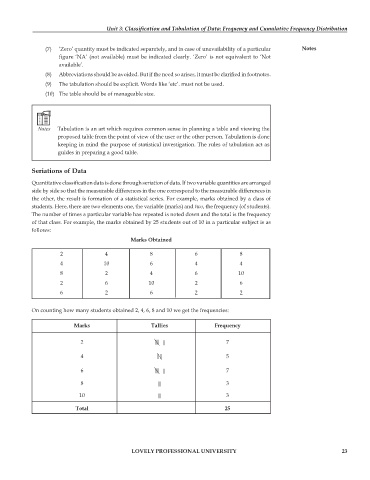
Quantitative classification data is done through seriation of data. If two variable quantities are arranged
side by side so that the measurable differences in the one correspond to the measurable differences in
the other, the result is formation of a statistical series. For example, marks obtained by a class of
students. Here, there are two elements one, the variable (marks) and two, the frequency (of students).
The number of times a particular variable has repeated is noted down and the total is the frequency
of that class. For example, the marks obtained by 25 students out of 10 in a particular subject is as
follows:
Marks Obtained
2 4 8 6 8
4 10 6 4 4
8 2 4 6 10
2 6 10 2 6
6 2 6 2 2
On counting how many students obtained 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 we get the frequencies:
Marks Tallies Frequency
2 |||| || 7
4 |||| 5
6 |||| || 7
8 ||| 3
10 ||| 3
Total 25
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 23