Page 27 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 27
Unit 3: Classification and Tabulation of Data: Frequency and Cumulative Frequency Distribution
Essential Parts of a Table Notes
In order to be complete and most informative, a table should have the following parts:
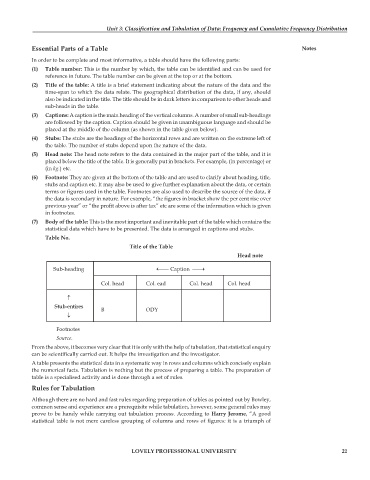
(1) Table number: This is the number by which, the table can be identified and can be used for
reference in future. The table number can be given at the top or at the bottom.
(2) Title of the table: A title is a brief statement indicating about the nature of the data and the
time-span to which the data relate. The geographical distribution of the data, if any, should
also be indicated in the title. The title should be in dark letters in comparison to other heads and
sub-heads in the table.
(3) Captions: A caption is the main heading of the vertical columns. A number of small sub-headings
are followed by the caption. Caption should be given in unambiguous language and should be
placed at the middle of the column (as shown in the table given below).
(4) Stubs: The stubs are the headings of the horizontal rows and are written on the extreme left of
the table. The number of stubs depend upon the nature of the data.
(5) Head note: The head note refers to the data contained in the major part of the table, and it is
placed below the title of the table. It is generally put in brackets. For example, (in percentage) or
(in kg.) etc.
(6) Footnote: They are given at the bottom of the table and are used to clarify about heading, title,
stubs and caption etc. It may also be used to give further explanation about the data, or certain
terms or figures used in the table. Footnotes are also used to describe the source of the data, if
the data is secondary in nature. For example, “the figures in bracket show the per cent rise over
previous year” or “the profit above is after tax” etc are some of the information which is given
in footnotes.
(7) Body of the table: This is the most important and inevitable part of the table which contains the
statistical data which have to be presented. The data is arranged in captions and stubs.
Table No.
Title of the Table
Head note
Sub-heading ←⎯⎯ Caption ⎯⎯→
Col. head Col. ead Col. head Col. head
↑
Stub-entires B ODY
↓
Footnotes
Source.
From the above, it becomes very clear that it is only with the help of tabulation, that statistical enquiry
can be scientifically carried out. It helps the investigation and the investigator.
A table presents the statistical data in a systematic way in rows and columns which concisely explain
the numerical facts. Tabulation is nothing but the process of preparing a table. The preparation of
table is a specialised activity and is done through a set of rules.
Rules for Tabulation
Although there are no hard and fast rules regarding preparation of tables as pointed out by Bowley,
common sense and experience are a prerequisite while tabulation, however, some general rules may
prove to be handy while carrying out tabulation process. According to Harry Jerome, “A good
statistical table is not mere careless grouping of columns and rows of figures: it is a triumph of
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 21