Page 31 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 31
Unit 3: Classification and Tabulation of Data: Frequency and Cumulative Frequency Distribution
Difference between Classification and Tabulation Notes
Some important points or differences between classification and tabulation are:
(1) Although both are necessary in statistical investigations, classification is done first and it forms
the basis for tabulation.
(2) Tabulation is a mechanical function of classification. But classification is not a mechanical
function.
(3) In classification, data are divided/classified in different classes as per similarities and
dissimilarities. Under tabulation this classified data is put in rows and columns.
(4) Classification involves analysis of data. Tabulation is the process of presenting the data.
Types of Tables
Following are the important types of tables:
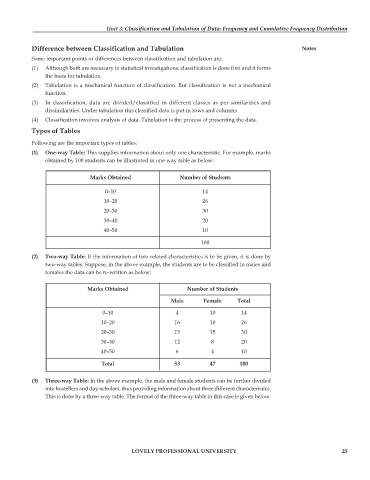
(1) One-way Table: This supplies information about only one characteristic. For example, marks
obtained by 100 students can be illustrated in one-way table as below:
Marks Obtained Number of Students
0–10 14
10–20 26
20–30 30
30–40 20
40–50 10
100
(2) Two-way Table: If the information of two related characteristics is to be given, it is done by
two-way tables. Suppose, in the above example, the students are to be classified in males and
females the data can be re-written as below:
Marks Obtained Number of Students
Male Female Total
0–10 4 10 14
10–20 16 10 26
20–30 15 15 30
30–40 12 8 20
40–50 6 4 10
Total 53 47 100
(3) Three-way Table: In the above example, the male and female students can be further divided
into hostellers and day-scholars, thus providing information about three different characteristics.
This is done by a three-way table. The format of the three-way table in this case is given below:
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 25