Page 81 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 81
Unit 6: Dispersion: Meaning and Characteristics, Absolute and Relative Measures of Dispersion including Range...
Notes
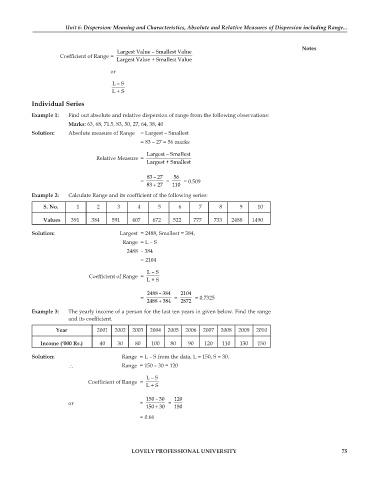
Largest Value – Smallest Value
Coefficient of Range =
Largest Value + Smallest Value
or
L – S
L + S
Individual Series
Example 1: Find out absolute and relative dispersion of range from the following observations:
Marks: 63, 68, 71.5, 83, 50, 27, 64, 38, 40
Solution: Absolute measure of Range = Largest – Smallest
= 83 – 27 = 56 marks
Largest – Smallest
Relative Measure =
Largest + Smallest
83 – 27 56
= = = 0.509
+
83 27 110
Example 2: Calculate Range and its coefficient of the following series:
S. No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Values 391 384 591 407 672 522 777 733 2488 1490
Solution: Largest = 2488, Smallest = 384,
Range = L – S
2488 – 384
= 2104
L – S
Coefficient of Range =
L + S
2488 – 384 2104
= = = 0.7325
+
2488 384 2872
Example 3: The yearly income of a person for the last ten years in given below. Find the range
and its coefficient.
Year 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010
Income (‘000 Rs.) 40 30 80 100 80 90 120 110 130 150
Solution: Range = L – S from the data, L = 150, S = 30.
∴ Range = 150 – 30 = 120
L – S
Coefficient of Range =
L + S
150 – 30 120
or = =
+
150 30 180
= 0.66
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 75