Page 83 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 83
Unit 6: Dispersion: Meaning and Characteristics, Absolute and Relative Measures of Dispersion including Range...
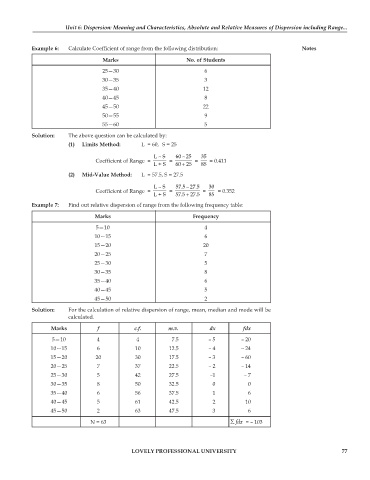
Example 6: Calculate Coefficient of range from the following distribution: Notes
Marks No. of Students
25—30 6
30—35 3
35—40 12
40—45 8
45—50 22
50—55 9
55—60 5
Solution: The above question can be calculated by:
(1) Limits Method: L = 60, S = 25
L – S 60 – 25 35
Coefficient of Range = = = = 0.411
+
L + S 60 25 85
(2) Mid-Value Method: L = 57.5, S = 27.5
L – S 57.5 – 27.5 30
Coefficient of Range = = = = 0.352
L + S 57.5 27.5 85
+
Example 7: Find out relative dispersion of range from the following frequency table:
Marks Frequency
5—10 4
10—15 6
15—20 20
20—25 7
25—30 5
30—35 8
35—40 6
40—45 5
45—50 2
Solution: For the calculation of relative dispersion of range, mean, median and mode will be
calculated.
Marks f c.f. m.v. dx fdx
5—10 4 4 7.5 – 5 – 20
10—15 6 10 12.5 – 4 – 24
15—20 20 30 17.5 – 3 – 60
20—25 7 37 22.5 – 2 – 14
25—30 5 42 27.5 –1 – 7
30—35 8 50 32.5 0 0
35—40 6 56 37.5 1 6
40—45 5 61 42.5 2 10
45—50 2 63 47.5 3 6
N = 63 ∑ fdx = – 103
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 77