Page 89 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 89
Unit 6: Dispersion: Meaning and Characteristics, Absolute and Relative Measures of Dispersion including Range...
Notes
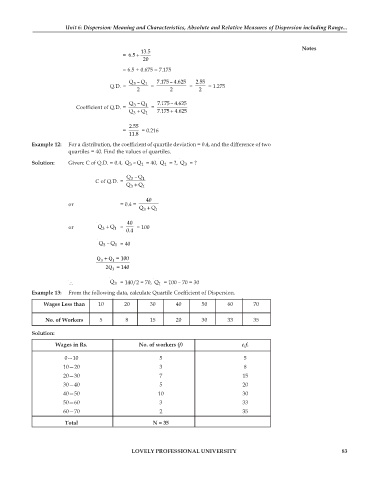
13.5
= 6.5 +
20
= 6.5 + 0.675 = 7.175
Q– Q 1 7.175 – 4.625 2.55
3
Q.D. = = = = 1.275
2 2 2
Q– Q 7.175 – 4.625
Coefficient of Q.D. = 3 1 =
+
Q + Q 1 7.175 4.625
3
2.55
= = 0.216
11.8
Example 12: For a distribution, the coefficient of quartile deviation = 0.4, and the difference of two
quartiles = 40. Find the values of quartiles.
Solution: Given: C of Q.D. = 0.4, Q– Q = 40, Q = ?, Q = ?
3
1
3
1
Q– Q
C of Q.D. = 3 1
Q + Q 1
3
40
or = 0.4 =
Q + Q 1
3
40
or Q + Q 1 = 0.4 = 100
3
Q– Q 1 = 40
3
Q + Q =100
3
1
2Q =140
3
∴ Q 3 = 140/2 = 70, Q = 100 – 70 = 30
1
Example 13: From the following data, calculate Quartile Coefficient of Dispersion.
Wages Less than 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
No. of Workers 5 8 15 20 30 33 35
Solution:
Wages in Rs. No. of workers (f) c.f.
0—10 5 5
10—20 3 8
20—30 7 15
30—40 5 20
40—50 10 30
50—60 3 33
60—70 2 35
Total N = 35
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 83