Page 93 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 93
Unit 6: Dispersion: Meaning and Characteristics, Absolute and Relative Measures of Dispersion including Range...
and then split into its integer component k and decimal component d, such that n = k + d. Notes
Then v is calculated as:
P
⎧ v , forn = 1
⎪ 1
⎪
v
v = ⎨ N, forn = N
P
⎪
v + ( ⎪ ⎩ k − d v v k ) k+1 = , < for1 n < N
The primary method recommended by NIST is similar to that given above, but with the rank calculated
as
P
n = ( + 1 )N
100
These two approaches give the rank of the 40 percentile in the above example as, respectively:
th
40
n = ( ) − 51 + 1 = 2.6
100
and
40
) +
n = ( 51 = 2.4
100
The values are then interpolated as usual based on these ranks, yielding 29 and 26, respectively, for
the 40 percentile.
th
Applications
When ISPs bill “burstable” internet bandwidth, the 95 or 98 percentile usually cuts off the top 5%
th
th
or 2% of bandwidth peaks in each month, and then bills at the nearest rate. In this way infrequent
peaks are ignored, and the customer is charged in a fairer way. The reason this statistic is so useful in
measuring data through put is that it gives a very accurate picture of the cost of the bandwidth. The
95 percentile says that 95% of the time, the usage is below this amount. Just the same, the remaining
th
5% of the time, the usage is above that amount.
Physicians will often use infant and children’s weight and height percentile to assess their growth
in comparison to national averages.
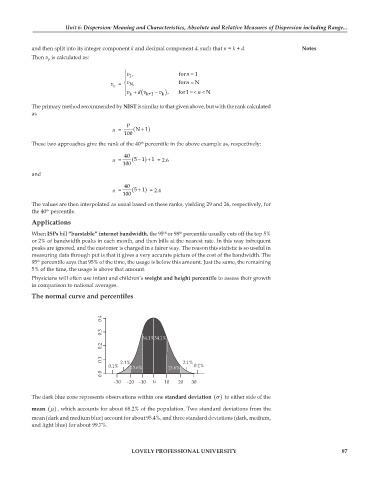
The normal curve and percentiles
0.4
0.3
34.1%34.1%
0.2
0.1 2.1% 2.1%
0.1% 13.6% 13.6% 0.1%
0.0
–30 –20 –10 10 20 30
σ
The dark blue zone represents observations within one standard deviation () to either side of the
mean () μ , which accounts for about 68.2% of the population. Two standard deviations from the
mean (dark and medium blue) account for about 95.4%, and three standard deviations (dark, medium,
and light blue) for about 99.7%.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 87