Page 218 - DEDU504_EDUCATIONAL_MEASUREMENT_AND_EVALUATION_ENGLISH
P. 218
Educational Measurement and Evaluation
Notes multiply score on term test by 10, making the mean 30 (3.0 × 10) and standard deviation 5.0
(0.5 × 10). Now the two S.D. are in the ratio 2:1 [60 and 30 mean] and [ 10 and 5 S.D.] for the
test and the term paper.
3. How many categories should be used
Reporting can be done in terms of 2 (pass-fail or mastery and non-mastery), 3 (A, B, F/C) or
4 (A, B, C, F/D) or 5 (A, B, C, D, F/E), 7, 9, ... or 100 or 101 categories. As the number of
categories increase, the number of borderline decisions increases correspondingly, but each
decision becomes less crucial for total academic record of students. There is a trade off of
increased frequency of potential error or unfairness in grading for decreased size and
importance of that error. The number of categories for grading is related to reliability of
evidence on which decisions are taken. If standard error of measurement is large in a
component that enters into a final grade or grade itself relative to the unit, discriminations
become meaningless (Table 1).
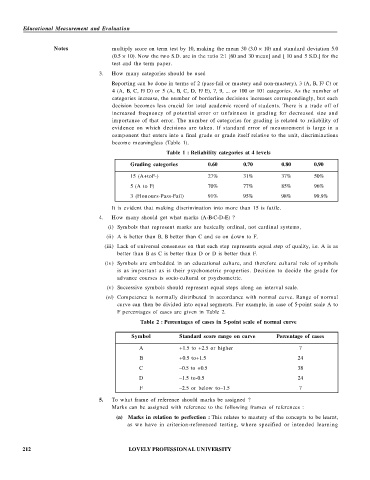
Table 1 : Reliability categories at 4 levels
Grading categories 0.60 0.70 0.80 0.90
15 (A+toF-) 27% 31% 37% 50%
5 (A to F) 70% 77% 85% 96%
3 (Honours-Pass-Fail) 91% 95% 98% 99.9%
It is evident that making discrimination into more than 15 is futile.
4. How many should get what marks (A-B-C-D-E) ?
(i) Symbols that represent marks are basically ordinal, not cardinal systems,
(ii) A is better than B, B better than C and so on down to F.
(iii) Lack of universal consensus on that each step represents equal step of quality, i.e. A is as
better than B as C is better than D or D is better than F.
(iv) Symbols are embedded in an educational culture, and therefore cultural role of symbols
is as important as is their psychometric properties. Decision to decide the grade for
advance courses is socio-cultural or psychometric.
(v) Successive symbols should represent equal steps along an interval scale.
(vi) Competence is normally distributed in accordance with normal curve. Range of normal
curve can then be divided into equal segments. For example, in case of 5-point scale A to
F percentages of cases are given in Table 2.
Table 2 : Percentages of cases in 5-point scale of normal curve
Symbol Standard score range on curve Percentage of cases
A +1.5 to +2.5 or higher 7
B +0.5 to+1.5 24
C –0.5 to +0.5 38
D –1.5 to-0.5 24
F –2.5 or below to–1.5 7
5. To what frame of reference should marks be assigned ?
Marks can be assigned with reference to the following frames of references :
(a) Marks in relation to perfection : This relates to mastery of the concepts to be learnt,
as we have in criterion-referenced testing, where specified or intended learning
212 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY