Page 247 - DEDU504_EDUCATIONAL_MEASUREMENT_AND_EVALUATION_ENGLISH
P. 247
Unit 20 : Methods of Feedback for Students
discussion groups. For the purposes of this Guide, the term ‘discussion group’ is used generically; Notes
however, discussion groups can take various forms, as exemplified by the list outlined above in
Nottingham Trent University’s Staff Resource Pack.
Discussion groups are less commonly used in institutions because they can be resource intensive
and require specialist training of staff to be effective. They provide an alternative to questionnaires
and student representation (although not necessarily a replacement) and can be a rich source of
information. Indeed, some institutions use these mechanisms in order to find out what students
think about the use of a particular mechanisms for gathering student feedback (for example, the
London School of Economics has used focus groups to investigate students’ views about the
issues surrounding an online questionnaire) or what questions students believe should be part of
a questionnaire survey (as used for the University of Central England’s student satisfaction survey).
We believe that the use of discussion groups in certain specific circumstances should be considered
and Section four of this Guide includes a discussion of these techniques.
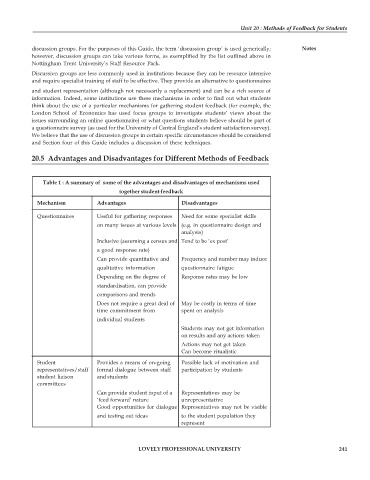
20.5 Advantages and Disadvantages for Different Methods of Feedback
Table 1 : A summary of some of the advantages and disadvantages of mechanisms used
together student feedback
Mechanism Advantages Disadvantages
Questionnaires Useful for gathering responses Need for some specialist skills
on many issues at various levels (e.g. in questionnaire design and
analysis)
Inclusive (assuming a census and Tend to be ‘ex post’
a good response rate)
Can provide quantitative and Frequency and number may induce
qualitative information questionnaire fatigue
Depending on the degree of Response rates may be low
standardisation, can provide
comparisons and trends
Does not require a great deal of May be costly in terms of time
time commitment from spent on analysis
individual students
Students may not get information
on results and any actions taken
Actions may not get taken
Can become ritualistic
Student Provides a means of on-going Possible lack of motivation and
representatives/staff formal dialogue between staff participation by students
student liaison and students
committees
Can provide student input of a Representatives may be
‘feed forward’ nature unrepresentative
Good opportunities for dialogue Representatives may not be visible
and testing out ideas to the student population they
represent
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 241