Page 57 - DEDU504_EDUCATIONAL_MEASUREMENT_AND_EVALUATION_ENGLISH
P. 57
Unit 5 : Planning for Different Types of Test
The first recorded use of standardised testing occured in France at the and of the 19 century and Notes
th
the start of 20 century. France began to require all students attend some school and educators and
th
administratives fore saw the problem of special education. To assess the abilities of children, the
French Government Commissioned.
Therefore Simon and Affred Bient to study this issue. They came up with what we now call an “IQ
Test”.
5.3 Different Guidelines for Planning a Test
There are various guides that are helpful is focussing attention beyond the knowledge level. They
are as follows :
5.3.1 Bloom Taxonomy
The learning competencies measured by a test should faithfully reflect the objectives of instruction.
Thus requires the identification of those instructional objectives to be measured by a test and then
clearly stating them in performance terms.
One useful guide is the cognitive domain of the Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, also known as
Bloom Taxonomy. This is an older guide one. It contains range types of learning competencies to
consider when planning a test. The cognitive domain involves knowledge and the development of
intellectual skills. This includes the recall or recognition of specific facts, procedural patterns, and
concepts that serve in the development of intellectual abilities and skills. There are six major categories
as follows :
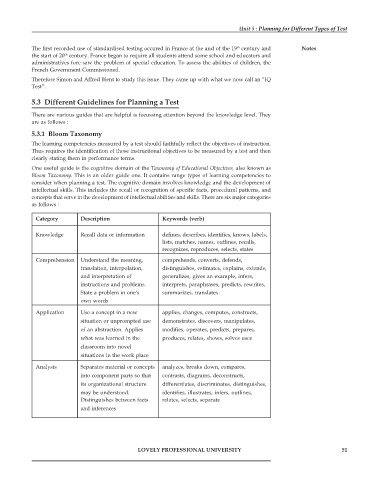
Category Description Keywords (verb)
Knowledge Recall data or information defines, describes, identifies, knows, labels,
lists, matches, names, outlines, recalls,
recognizes, reproduces, selects, states
Comprehension Understand the meaning, comprehends, converts, defends,
translation, interpolation, distinguishes, estimates, explains, extends,
and interpretation of generalizes, gives an example, infers,
instructions and problems. interprets, paraphrases, predicts, rewrites,
State a problem in one's summarizes, translates
own words
Application Use a concept in a new applies, changes, computes, constructs,
situation or unprompted use demonstrates, discovers, manipulates,
of an abstraction. Applies modifies, operates, predicts, prepares,
what was learned in the produces, relates, shows, solves uses
classroom into novel
situations in the work place
Analysis Separates material or concepts analyzes, breaks down, compares,
into component parts so that contrasts, diagrams, deconstructs,
its organizational structure differentiates, discriminates, distinguishes,
may be understood. identifies, illustrates, infers, outlines,
Distinguishes between facts relates, selects, separate
and inferences
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 51