Page 64 - DMTH404_STATISTICS
P. 64
Statistics
Notes
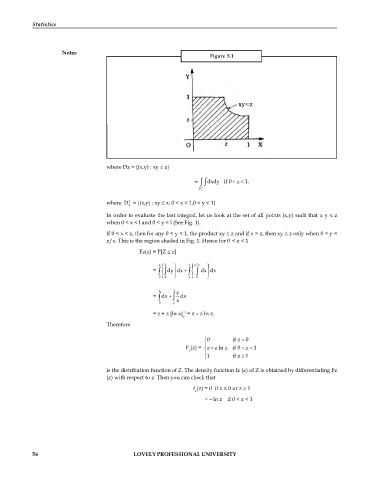
Figure 5.1
where Dz = {(x,y) : xy z}
dxdy if 0 z 1.
1
D
z
1
where D = {(x,y) : xy z, 0 < x < 1,0 < y < 1}
z
In order to evaluate the last integral, let us look at the set of all points (x,y) such that x y z
when 0 < x < l and 0 < y < l (See Fig. 1).
If 0 < x < z, then for any 0 < y < 1, the product xy z and if x > z, then xy z only when 0 < y <
z/x. This is the region shaded in Fig. 1. Hence for 0 < z < 1
Fz(z) = P[Z z]
z 1 1 z /x
= dy dx dx dx
0 0 z 0
z 1 z
= dx dx
0 z x
1
= z + z [ln x] = z – z ln z.
z
Therefore
0 if z 0
F (z) = z z ln z if 0 z 1
z
1 if z 1
is the distribution function of Z. The density function fz (z) of Z is obtained by differentiating Fz
(z) with respect to z. Then you can check that
f (z) = 0 if z 0 or z 1
z
= – ln z if 0 < z < 1
56 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY