Page 65 - DMTH404_STATISTICS
P. 65
Unit 5: Functions of Random Variables
Notes
Example 2: Suppose X and Y are independent exponential random variables with the
density function
y
-x
f (x) = e , x > 0 and f(y) = e , y > 0
= 0 , x 0. = 0, y 0
Define Z = X + Y and let us find the distribution function of Z.
From the definition of Z,
Fz(z) = P[Z z] = 0 if z < 0
and, for z > 0
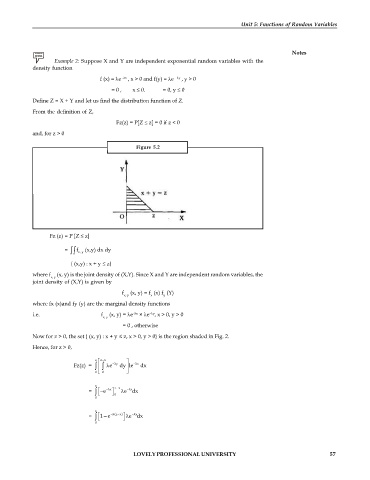
Figure 5.2
Fz (z) = P [Z z]
= f x, y (x,y) dx dy
{ (x,y) : x + y z}
where f (x, y) is the joint density of (X,Y). Since X and Y are independent random variables, the
x, y
joint density of (X,Y) is given by
f (x, y) = f (x) f (Y)
x, y x y
where fx (x)and fy (y) are the marginal density functions
i.e. f (x, y) = e × e , x > 0, y > 0
–x
y
x, y
= 0 , otherwise
Now for z > 0, the set { (x, y) : x + y z, x > 0, y > 0} is the region shaded in Fig. 2.
Hence, for z > 0,
z z x
Fz(z) = e y dy le – x dx
0 0
z z x
= e x 0 e – x dx
0
z
= 1 e (z x) e – x dx
0
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 57