Page 200 - DSOC404_METHODOLOGY_OF_SOCIAL_RESEARCH_ENGLISH
P. 200
Methodology of Social Research
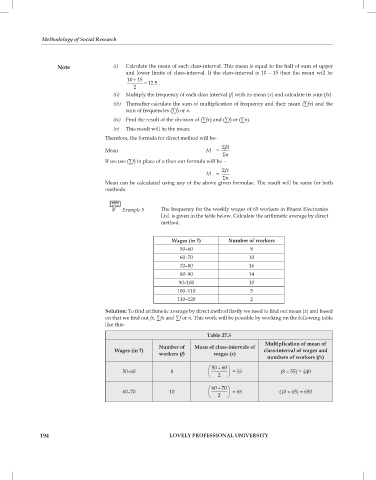
note (i) Calculate the mean of each class-interval. this mean is equal to the half of sum of upper
and lower limits of class-interval. if the class-interval is 10 – 15 then the mean will be
10 15 = 12.5 .
+
2
(ii) Multiply the frequency of each class interval (f) with its mean (x) and calculate its sum (fx)
(iii) Thereafter calculate the sum of multiplication of frequency and their mean (∑fx) and the
sum of frequencies (∑f) or n.
(iv) Find the result of the division of (∑fx) and (∑f) or (∑n).
(v) this result will be the mean.
therefore, the formula for direct method will be-
S fd
Mean M =
S n
If we use (∑f) in place of n then our formula will be –
S fx
M =
S n
Mean can be calculated using any of the above given formulae. the result will be same for both
methods.
Example 5 the frequency for the weekly wages of 65 workers in Bharat electronics
Ltd. is given in the table below. Calculate the arithmetic average by direct
method.
Wages (in `) number of workers
50–60 8
60–70 10
70–80 16
80–90 14
90–100 10
100–110 5
110–120 2
solution: To find arithmetic average by direct method firstly we need to find out mean (x) and based
on that we find out fx, ∑fx and ∑f or n. this work will be possible by working on the following table
like this-
table 27.3
Multiplication of mean of
number of Mean of class-intervals of
Wages (in `) class-interval of wages and
workers (f) wages (x)
numbers of workers (fx)
50 60 +
50–60 8 = 55 (8 × 55) = 440
2
60 70 +
60–70 10 = 65 (10 × 65) = 650
2
194 loVely professional uniVersity