Page 48 - DENG102_COMMUNICATION_SKILLS_II
P. 48
Unit 3: Conversation Building
3.1.2 oral fluency Development notes
In business transactions that involve face to face interaction between individuals or groups of
individuals, it is not enough to be able to talk, speak, discuss, argue or negotiate an issue. A
manager should be able to converse or discuss persuasively, effectively and convincingly. To do
so, he must know the skills of oral communication. Oral communication skills should include the
following abilities:
1. Help in problem solving.
2. Resolve conflict.
3. Influence people to work together.
4. Persuade others to be involved in organizational goals.
5. Be assertive without being aggressive.
6. Develop listening skills.
7. Be an effective negotiator.
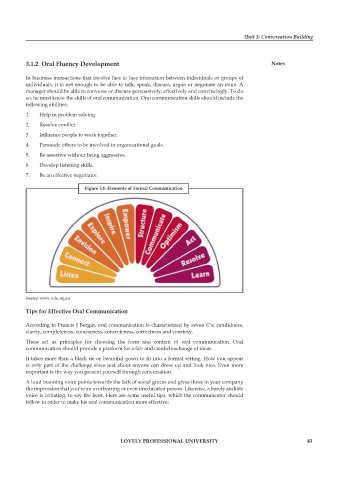
figure 3.1: elements of formal communication
Source: www.ncls.org.au
tips for effective oral communication
According to Francis J Bergin, oral communication is characterized by seven C’s: candidness,
clarity, completeness, conciseness, concreteness, correctness and courtesy.
These act as principles for choosing the form and content of oral communication. Oral
communication should provide a platform for a fair and candid exchange of ideas.
It takes more than a black tie or beautiful gown to fit into a formal setting. How you appear
is only part of the challenge since just about anyone can dress up and look nice. Even more
important is the way you present yourself through conversation.
A loud booming voice points towards the lack of social graces and gives those in your company
the impression that you’re an overbearing or even uneducated person. Likewise, a barely audible
voice is irritating, to say the least. Here are some useful tips, which the communicator should
follow in order to make his oral communication more effective:
lovely Professional university 43