Page 100 - DCOM202_COST_ACCOUNTING_I
P. 100
Cost Accounting – I
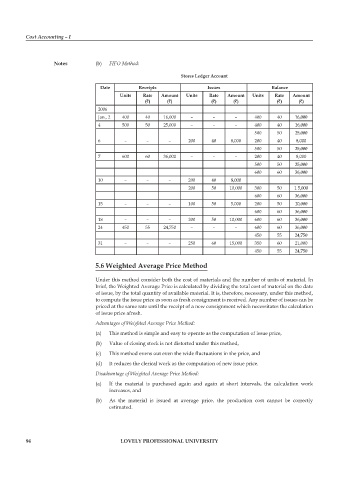
Notes (b) FIFO Method:
Stores Ledger Account
date Receipts Issues Balance
Units Rate Amount Units Rate Amount Units Rate Amount
(`) (`) (`) (`) (`) (`)
2006
Jan., 2 400 40 16,000 – – – 400 40 16,000
4 500 50 25,000 – – – 400 40 16,000
500 50 25,000
6 – – – 200 40 8,000 200 40 8,000
500 50 25,000
7 600 60 36,000 – – – 200 40 8,000
500 50 25,000
600 60 36,000
10 – – – 200 40 8,000
200 50 10,000 300 50 1 5,000
600 60 36,000
15 – – – 100 50 5,000 200 50 10,000
600 60 36,000
18 – – – 200 50 10,000 600 60 36,000
24 450 55 24,750 – – – 600 60 36,000
450 55 24,750
31 – – – 250 60 15,000 350 60 21,000
450 55 24,750
5.6 Weighted Average Price Method
Under this method consider both the cost of materials and the number of units of material. In
brief, the Weighted Average price is calculated by dividing the total cost of material on the date
of issue, by the total quantity of available material. It is, therefore, necessary, under this method,
to compute the issue price as soon as fresh consignment is received. Any number of issues can be
priced at the same rate until the receipt of a new consignment which necessitates the calculation
of issue price afresh.
Advantages of Weighted Average Price Method:
(a) This method is simple and easy to operate as the computation of issue price,
(b) Value of closing stock is not distorted under this method,
(c) This method evens out even the wide fluctuations in the price, and
(d) It reduces the clerical work as the computation of new issue price.
Disadvantage of Weighted Average Price Method:
(a) If the material is purchased again and again at short intervals, the calculation work
increases, and
(b) As the material is issued at average price, the production cost cannot be correctly
estimated.
94 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY