Page 103 - DCOM202_COST_ACCOUNTING_I
P. 103
Unit 5: Methods of Valuing Material Issues
Notes
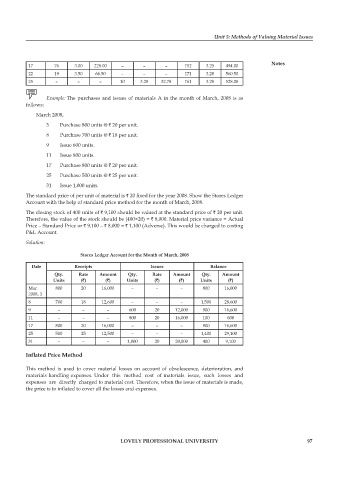
17 76 3.00 228.00 – – – 152 3.25 494.00
22 19 3.50 66.50 – – – 171 3.28 560.50
25 – – – 10 3.28 32.78 161 3.28 528.08
Example: The purchases and issues of materials A in the month of March, 2008 is as
follows:
March 2008,
3 purchase 800 units @ ` 20 per unit.
8 purchase 700 units @ ` 18 per unit.
9 Issue 600 units.
11 Issue 800 units.
17 purchase 800 units @ ` 20 per unit.
25 purchase 500 units @ ` 25 per unit.
31 Issue 1,000 units.
The standard price of per unit of material is ` 20 fixed for the year 2008. Show the Stores Ledger
Account with the help of standard price method for the month of March, 2008.
The closing stock of 400 units of ` 9,100 should be valued at the standard price of ` 20 per unit.
Therefore, the value of the stock should be (400×20) = ` 8,000. Material price variance = Actual
price – Standard price or ` 9,100 – ` 8,000 = ` 1,100 (Adverse). This would be charged to costing
p&L Account.
Solution:
Stores Ledger Account for the Month of March, 2008
date Receipts Issues Balance
Qty. Rate Amount Qty. Rate Amount Qty. Amount
Units (`) (`) Units (`) (`) Units (`)
Mar. 800 20 16,000 – – – 800 16,000
2008, 3
8 700 18 12,600 – – – 1,500 28,600
9 – – – 600 20 12,000 900 16,600
11 – – – 800 20 16,000 100 600
17 800 20 16,000 – – – 900 16,600
25 500 25 12,500 – – – 1,400 29,100
31 – – – 1,000 20 20,000 400 9,100
Inflated Price Method
This method is used to cover material losses on account of obsolescence, deterioration, and
materials handling expenses. Under this method cost of materials issue, such losses and
expenses are directly charged to material cost. Therefore, when the issue of materials is made,
the price is to inflated to cover all the losses and expenses.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 97