Page 98 - DCOM202_COST_ACCOUNTING_I
P. 98
Cost Accounting – I
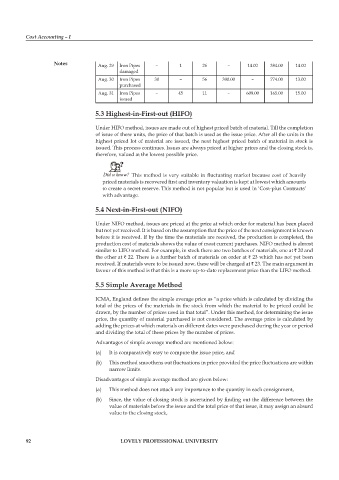
Notes Aug. 29 Iron pipes – 1 26 – 14.00 384.00 14.00
damaged
Aug. 30 Iron pipes 30 – 56 390.00 – 774.00 13.00
purchased
Aug. 31 Iron pipes – 45 11 – 609.00 165.00 15.00
issued
5.3 Highest-in-First-out (HIFO)
Under HIFO method, issues are made out of highest priced batch of material. Till the completion
of issue of these units, the price of that batch is used as the issue price. After all the units in the
highest priced lot of material are issued, the next highest priced batch of material in stock is
issued. This process continues. Issues are always priced at higher prices and the closing stock is,
therefore, valued at the lowest possible price.
Did u know? This method is very suitable in fluctuating market because cost of heavily
priced materials is recovered first and inventory valuation is kept at lowest which amounts
to create a secret reserve. This method is not popular but is used in ‘Cost-plus Contracts’
with advantage.
5.4 Next-in-First-out (NIFO)
Under NIFO method, issues are priced at the price at which order for material has been placed
but not yet received. It is based on the assumption that the price of the next consignment is known
before it is received. If by the time the materials are received, the production is completed, the
production cost of materials shows the value of most current purchases. NIFO method is almost
similar to LIFO method. For example, in stock there are two batches of materials, one at ` 20 and
the other at ` 22. There is a further batch of materials on order at ` 23 which has not yet been
received. If materials were to be issued now, these will be charged at ` 23. The main argument in
favour of this method is that this is a more up-to-date replacement price than the LIFO method.
5.5 Simple Average Method
ICMA, England defines the simple average price as “a price which is calculated by dividing the
total of the prices of the materials in the stock from which the material to be priced could be
drawn, by the number of prices used in that total”. Under this method, for determining the issue
price, the quantity of material purchased is not considered. The average price is calculated by
adding the prices at which materials on different dates were purchased during the year or period
and dividing the total of these prices by the number of prices.
Advantages of simple average method are mentioned below:
(a) It is comparatively easy to compute the issue price, and
(b) This method smoothens out fluctuations in price provided the price fluctuations are within
narrow limits.
Disadvantages of simple average method are given below:
(a) This method does not attach any importance to the quantity in each consignment,
(b) Since, the value of closing stock is ascertained by finding out the difference between the
value of materials before the issue and the total price of that issue, it may assign an absurd
value to the closing stock,
92 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY