Page 71 - DCOM202_COST_ACCOUNTING_I
P. 71
Unit 4: Material Control
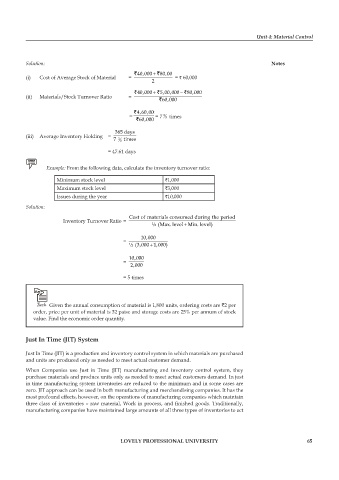
Solution: Notes
,
,
`40 000 + `80 00
(i) Cost of Average Stock of Material = = ` 60,000
2
`40 000 + , `500 000 − , , `80 000
,
(ii) Materials/Stock Turnover Ratio = `60 000
,
`460 000
,
,
= = 7 2 3 times
,
`60 000
365 days
(iii) Average Inventory Holding =
7 times
2
3
= 47.61 days
Example: From the following data, calculate the inventory turnover ratio:
Minimum stock level `1,000
Maximum stock level `3,000
Issues during the year `10,000
Solution:
Cost of materialsconsumedduringthe period
Inventory Turnover Ratio =
½( Maxlevel + MMinlevel. )
.
,
10 000
=
,
+
½( 3 000 1 000)
,
,
10 000
=
2 000
,
= 5 times
Task Given the annual consumption of material is 1,800 units, ordering costs are `2 per
order, price per unit of material is 32 paise and storage costs are 25% per annum of stock
value. Find the economic order quantity.
Just In Time (JIT) System
Just In Time (JIT) is a production and inventory control system in which materials are purchased
and units are produced only as needed to meet actual customer demand.
When Companies use Just in Time (JIT) manufacturing and inventory control system, they
purchase materials and produce units only as needed to meet actual customers demand. In just
in time manufacturing system inventories are reduced to the minimum and in some cases are
zero. JIT approach can be used in both manufacturing and merchandising companies. It has the
most profound effects, however, on the operations of manufacturing companies which maintain
three class of inventories – raw material, Work in process, and finished goods. Traditionally,
manufacturing companies have maintained large amounts of all three types of inventories to act
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 65