Page 69 - DCOM202_COST_ACCOUNTING_I
P. 69
Unit 4: Material Control
Notes
Did u know? What is trade discount?
Trade discount is the discount granted by the supplier to the buyer of materials at the
moment of bulk purchase. This % of discount is greatly possible only during the periods of
greater volume of purchase, which reduces the overall cost of the acquisition.
If the quantity is procured in lesser volume, the following are construed as advantages:
z z The carrying cost will come down in the case of lesser inventories.
z z The cost of storage is lesser as far as the lesser quantities of materials.
z z Loss due to deterioration, obsolescence, wastage will be minimum.
z z Insurance cost is less due to lesser volume of materials.
Tabular Method
When there are quantity discounts offered by the supplier at different lot sizes purchased i.e.
purchase price of material varies at different quantity levels, the tabular method is used to
determine Economic Order Quantity. It is illustrated in the below example:
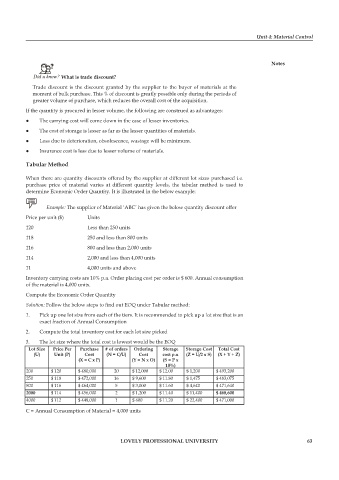
Example: The supplier of Material ‘ABC’ has given the below quantity discount offer
price per unit ($) Units
120 Less than 250 units
118 250 and less than 800 units
116 800 and less than 2,000 units
114 2,000 and less than 4,000 units
11 4,000 units and above
Inventory carrying costs are 10% p.a. Order placing cost per order is $ 600. Annual consumption
of the material is 4,000 units.
Compute the Economic Order Quantity
Solution: Follow the below steps to find out EOQ under Tabular method:
1. Pick up one lot size from each of the tiers. It is recommended to pick up a lot size that is an
exact fraction of Annual Consumption
2. Compute the total inventory cost for each lot size picked
3. The lot size where the total cost is lowest would be the EOQ
Lot Size Price Per Purchase # of orders Ordering Storage Storage Cost Total Cost
(U) Unit (P) Cost (N = C/U) Cost cost p.u (Z = U/2 x S) (X + Y + Z)
(X = C x P) (Y = N x O) (S = P x
10%)
200 $ 120 $ 480,000 20 $ 12,000 $ 12.00 $ 1,200 $ 493,200
250 $ 118 $ 472,000 16 $ 9,600 $ 11.80 $ 1,475 $ 483,075
800 $ 116 $ 464,000 5 $ 3,000 $ 11.60 $ 4,640 $ 471,640
2000 $ 114 $ 456,000 2 $ 1,200 $ 11.40 $ 11,400 $ 468,600
4000 $ 112 $ 448,000 1 $ 600 $ 11.20 $ 22,400 $ 471,000
C = Annual Consumption of Material = 4,000 units
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 63