Page 69 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 69
Quantitative Techniques – I
Notes
Task “Diagrams do not add anything to the meaning of statistics but when drawn and
studied intelligently they bring to view the salient characteristics of groups and series”.
Justify it.
Did u know? A sub-divided or percentage sub-divided bar diagram is also known as a
stacked bar diagram.
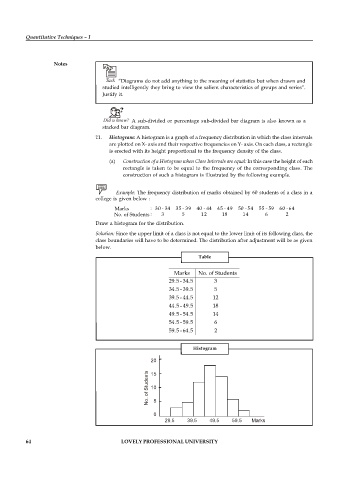
11. Histogram: A histogram is a graph of a frequency distribution in which the class intervals
are plotted on X- axis and their respective frequencies on Y- axis. On each class, a rectangle
is erected with its height proportional to the frequency density of the class.
(a) Construction of a Histogram when Class Intervals are equal: In this case the height of each
rectangle is taken to be equal to the frequency of the corresponding class. The
construction of such a histogram is illustrated by the following example.
Example: The frequency distribution of marks obtained by 60 students of a class in a
college is given below :
Marks : 30 - 34 35 - 39 40 - 44 45 - 49 50 - 54 55 - 59 60 - 64
No. of Students : 3 5 12 18 14 6 2
Draw a histogram for the distribution.
Solution: Since the upper limit of a class is not equal to the lower limit of its following class, the
class boundaries will have to be determined. The distribution after adjustment will be as given
below.
Table
Marks No. of Students
29.5- 34.5 3
34.5 - 39.5 5
39.5 - 44.5 12
44.5 - 49.5 18
49.5- 54.5 14
54.5 - 59.5 6
59.5 -64.5 2
Histogram
20
No. of Students 15
10
5
0
29.5 39.5 49.5 59.5 Marks
64 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY