Page 13 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 13
Cost Accounting – II
Notes Problem 2:
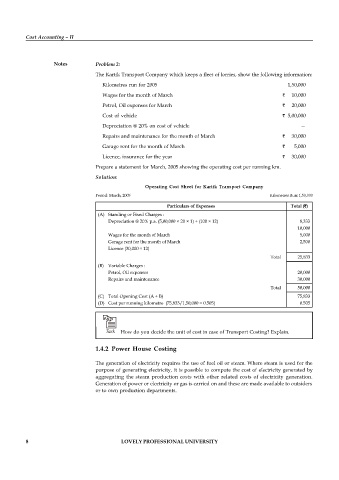
The Kartik Transport Company which keeps a fleet of lorries, show the following information:
Kilometres run for 2005 1,50,000
Wages for the month of March ` 10,000
Petrol, Oil expenses for March ` 20,000
Cost of vehicle ` 5,00,000
Depreciation @ 20% on cost of vehicle —
Repairs and maintenance for the month of March ` 30,000
Garage rent for the month of March ` 5,000
Licence, insurance for the year ` 30,000
Prepare a statement for March, 2005 showing the operating cost per running km.
Solution:
Operating Cost Sheet for Kartik Transport Company
Period: March, 2005 Kilometres Run: 1,50,000
Particulars of Expenses Total (`)
(A) Standing or Fixed Charges :
Depreciation @ 20% p.a. (5,00,000 × 20 × 1) ÷ (100 × 12) 8,333
10,000
Wages for the month of March 5,000
Garage rent for the month of March 2,500
Licence (30,000 ÷ 12)
Total 25,833
(B) Variable Charges :
Petrol, Oil expenses 20,000
Repairs and maintenance 30,000
Total 50,000
(C) Total Opening Cost (A + B) 75,833
(D) Cost per running kilometre (75,833/1,50,000 = 0.505) 0.505
Task How do you decide the unit of cost in case of Transport Costing? Explain.
1.4.2 Power House Costing
The generation of electricity requires the use of fuel oil or steam. Where steam is used for the
purpose of generating electricity, it is possible to compute the cost of electricity generated by
aggregating the steam production costs with other related costs of electricity generation.
Generation of power or electricity or gas is carried on and these are made available to outsiders
or to own production departments.
8 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY