Page 153 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 153
Cost Accounting – II
Notes 8.3.2 Disadvantages
The disadvantages of cost audit are as follows:
(i) Cost audit involves cost of products and this may not be suitable for small industries,
(ii) Cost audit may create unnecessary problems in day-to-day official work,
(iii) When the financial and other related accounts are audited, audit of cost accounts is
unnecessary work in the audit practice,
(iv) When the various cost and other accounts are prepared or maintained by a qualified
accountant, there can be no reason for getting such accounts audited by another auditor,
and
(v) The cost auditor may be a qualified man, but he may not be always right and correct
opinion regarding various accounts and its information.
8.3.3 Difference between Financial Audit and Cost Audit
In general, no difference between financial and cost audit is discernible. Both employ the similar
methods, techniques and principles for examining the various accounts. Financial audit and
Cost audit may be distinguished as follows:
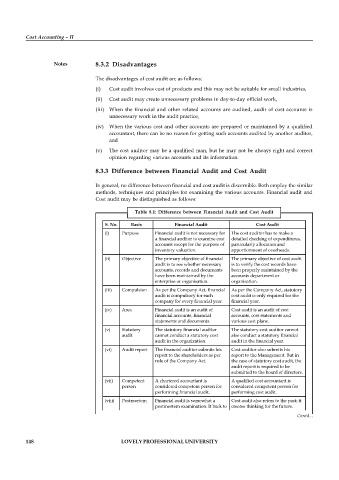
Table 8.1: Difference between Financial Audit and Cost Audit
S. No. Basis Financial Audit Cost Audit
(i) Purpose Financial audit is not necessary for The cost auditor has to make a
a financial auditor to examine cost detailed checking of expenditures,
accounts except for the purpose of particularly allocation and
inventory valuation. apportionment of overheads.
(ii) Objective The primary objective of financial The primary objective of cost audit
audit is to see whether necessary is to verify the cost records have
accounts, records and documents been properly maintained by the
have been maintained by the accounts department or
enterprise or organisation. organisation.
(iii) Compulsion As per the Company Act, financial As per the Company Act, statutory
audit is compulsory for each cost audit is only required for the
company for every financial year. financial year.
(iv) Area Financial audit is an audit of Cost audit is an audit of cost
financial accounts, financial accounts, cost statements and
statements and documents. various cost plans.
(v) Statutory The statutory financial auditor The statutory cost auditor cannot
audit cannot conduct a statutory cost also conduct a statutory financial
audit in the organization. audit in the financial year.
(vi) Audit report The financial auditor submits his Cost auditor also submits his
report to the shareholders as per report to the Management. But in
rule of the Company Act. the case of statutory cost audit, the
audit report is required to be
submitted to the board of directors.
(vii) Competent A chartered accountant is A qualified cost accountant is
person considered competent person for considered competent person for
performing financial audit. performing cost audit.
(viii) Postmortem Financial audit is somewhat a Cost audit also refers to the past; it
postmortem examination. It back to creates thinking for the future.
the past of company or
organization. Contd...
(ix) Share- Financial audit is essentially an Cost audit is in the hands of
holders and audit on behalf of the share management and also conducted
management holders. on behalf of the management.
148 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY
(x) Inventory In the matter of stock or inventory, The cost auditor has to not only
checking the financial auditor has only to see check the cost of each item of stock
whether all categories of stocks or or inventory, but also see whether
inventories have been included in the inventories of materials have
the accounts. been included in the proper way.