Page 216 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 216
Unit 12: Standard Costing
different periods or levels of activity may fluctuate widely and may adversely affect profit Notes
figure.
Historical costing does not help to detect mistakes and inefficiencies leading to variation in
profit. The reasons for the cost fluctuation apart from volume variation may be detected by
introduction of standard costing. Standard costing is a very important device of cost control, as
it detects not only variation in volume but also variation in costs. That is to say, the standard
costing will highlight what a product should cost, and the reasons for the excess of actual costs
over that of what would have been. In brief, a standard costing helps in minimising costs as far
as practicable to enhance efficiency in performance by setting up standard for expenses and
performance of production.
12.1 Standard Cost and Standard Costing
In order to have a thorough understanding concepts related to standard cost and standard
costing should be well understood. First of all, let’s discuss the term ‘standard’.
The standard refers to an indicator which is used to evaluate performance, quality etc. According
to Eric L. Kohler, “Standard is a desired attainable objective, a performance, a good, a model.”
Usually, standard denotes a predetermined rate or amount against which actual performance in
activity is compared as a measure to evaluate. Standard rates, that a firm or industry applies, are
based on money, physical inputs and physical outputs of commodities. Standard are, therefore,
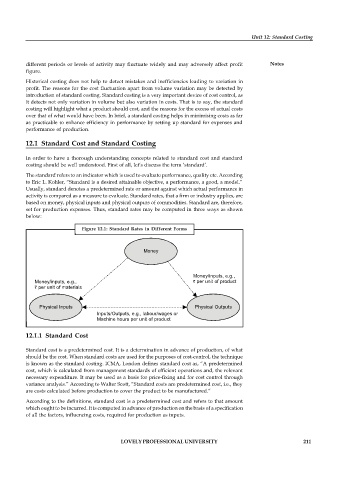
set for production expenses. Thus, standard rates may be computed in three ways as shown
below:
Figure 12.1: Standard Rates in Different Forms
Money
Money/inputs, e.g.,
Money/inputs, e.g., ` per unit of product
` per unit of materials
Physical Inputs Physical Outputs
Inputs/Outputs, e.g., labour/wages or
Machine hours per unit of product
12.1.1 Standard Cost
Standard cost is a predetermined cost. It is a determination in advance of production, of what
should be the cost. When standard costs are used for the purposes of cost-control, the technique
is known as the standard costing. ICMA, London defines standard cost as, “A predetermined
cost, which is calculated from management standards of efficient operations and, the relevant
necessary expenditure. It may be used as a basis for price-fixing and for cost control through
variance analysis.” According to Walter Scott, “Standard costs are predetermined cost, i.e., they
are costs calculated before production to cover the product to be manufactured.”
According to the definitions, standard cost is a predetermined cost and refers to that amount
which ought to be incurred. It is computed in advance of production on the basis of a specification
of all the factors, influencing costs, required for production as inputs.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 211