Page 52 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 52
Unit 3: Absorption Costing and Marginal Costing
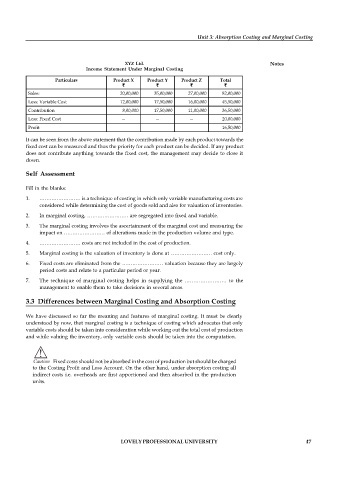
XYZ Ltd. Notes
Income Statement Under Marginal Costing
Particulars Product X Product Y Product Z Total
` ` ` `
Sales: 20,00,000 35,00,000 27,00,000 82,00,000
Less: Variable Cost 12,00,000 17,50,000 16,00,000 45,50,000
Contribution 8,00,000 17,50,000 11,00,000 36,50,000
Less: Fixed Cost — — — 20,00,000
Profit 16,50,000
It can be seen from the above statement that the contribution made by each product towards the
fixed cost can be measured and thus the priority for each product can be decided. If any product
does not contribute anything towards the fixed cost, the management may decide to close it
down.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. …………………… is a technique of costing in which only variable manufacturing costs are
considered while determining the cost of goods sold and also for valuation of inventories.
2. In marginal costing, …………………… are segregated into fixed and variable.
3. The marginal costing involves the ascertainment of the marginal cost and measuring the
impact on …………………… of alterations made in the production volume and type.
4. …………………… costs are not included in the cost of production.
5. Marginal costing is the valuation of inventory is done at …………………… cost only.
6. Fixed costs are eliminated from the …………………… valuation because they are largely
period costs and relate to a particular period or year.
7. The technique of marginal costing helps in supplying the …………………… to the
management to enable them to take decisions in several areas.
3.3 Differences between Marginal Costing and Absorption Costing
We have discussed so far the meaning and features of marginal costing. It must be clearly
understood by now, that marginal costing is a technique of costing which advocates that only
variable costs should be taken into consideration while working out the total cost of production
and while valuing the inventory, only variable costs should be taken into the computation.
!
Caution Fixed costs should not be absorbed in the cost of production but should be charged
to the Costing Profit and Loss Account. On the other hand, under absorption costing all
indirect costs i.e. overheads are first apportioned and then absorbed in the production
units.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 47