Page 39 - DCOM208_BANKING_THEORY_AND_PRACTICE
P. 39
Banking Theory and Practice
Notes 3.2 Classification of Banks in India
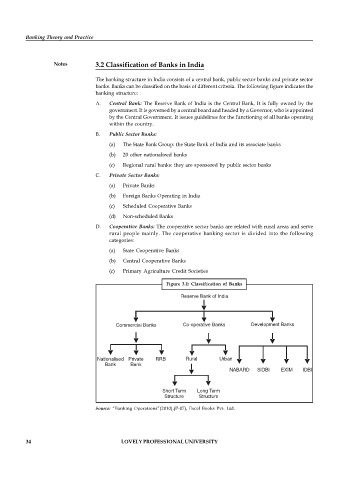
The banking structure in India consists of a central bank, public sector banks and private sector
banks. Banks can be classified on the basis of different criteria. The following figure indicates the
banking structure:
A. Central Bank: The Reserve Bank of India is the Central Bank. It is fully owned by the
government. It is governed by a central board and headed by a Governor, who is appointed
by the Central Government. It issues guidelines for the functioning of all banks operating
within the country.
B. Public Sector Banks:
(a) The State Bank Group: the State Bank of India and its associate banks
(b) 20 other nationalized banks
(c) Regional rural banks: they are sponsored by public sector banks
C. Private Sector Banks:
(a) Private Banks
(b) Foreign Banks Operating in India
(c) Scheduled Cooperative Banks
(d) Non-scheduled Banks
D. Cooperative Banks: The cooperative sector banks are related with rural areas and serve
rural people mainly. The cooperative banking sector is divided into the following
categories:
(a) State Cooperative Banks
(b) Central Cooperative Banks
(c) Primary Agriculture Credit Societies
Figure 3.1: Classification of Banks
Reserve Bank of India
Commercial Banks Co-operative Banks Development Banks
Nationalised Private RRB Rural Urban
Bank Bank
NABARD SIDBI EXIM IDBI
Short Term Long Term
Structure Structure
Source: “Banking Operations”(2010),(P-07), Excel Books Pvt. Ltd.
34 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY