Page 160 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 160
Unit 8: Standard Costing
(ii) Both techniques are based on the presumption that cost is controllable. Notes
(iii) In both the techniques, results of comparison are analysed and reported to management.
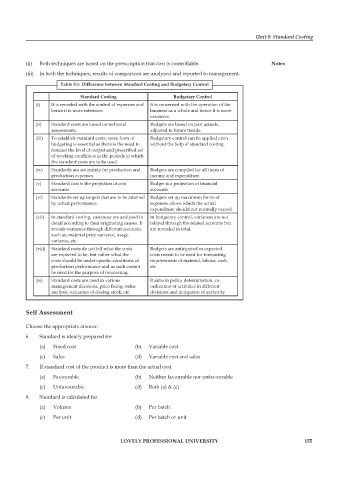
Table 8.1: Difference between Standard Costing and Budgetary Control
Standard Costing Budgetary Control
(i) It is revealed with the control of expenses and It is concerned with the operation of the
hence it is more intensive. business as a whole and hence it is more
extensive.
(ii) Standard costs are based on technical Budgets are based on past actuals,
assessments. adjusted to future trends.
(iii) To establish standard costs, some form of Budgetary control can be applied even
budgeting is essential as there is the need to without the help of standard costing.
forecast the level of output and prescribed set
of working conditions in the periods in which
the standard costs are to be used.
(iv) Standards are set mainly for production and Budgets are compiled for all items of
production expenses. income and expenditure.
(v) Standard cost is the projection of cost Budget is a projection of financial
accounts. accounts.
(vi) Standards set up targets that are to be attained Budgets set up maximum limits of
by actual performance. expenses above which the actual
expenditure should not normally exceed.
(vii) In standard costing, variances are analysed in In budgetary control, variances are not
detail according to their originating causes. It related through the related accounts but
reveals variances through different accounts, are revealed in total.
such as, material price variance, usage
variance, etc.
(viii) Standard costs do not tell what the costs Budgets are anticipated or expected
are expected to be, but rather what the costs meant to be used for forecasting
costs should be under specific conditions of requirements of material, labour, cash,
production performance and as such cannot etc.
be used for the purpose of forecasting.
(ix) Standard costs are used in various It aims in policy determination, co-
management decisions, price fixing, value ordination of activities in different
analysis, valuation of closing stock, etc. divisions and delegation of authority.
Self Assessment
Choose the appropriate answer:
6. Standard is ideally prepared for
(a) Fixed cost (b) Variable cost
(c) Sales (d) Variable cost and sales
7. If standard cost of the product is more than the actual cost
(a) Favourable (b) Neither favourable nor unfavourable
(c) Unfavourable (d) Both (a) & (c)
8. Standard is calculated for
(a) Volume (b) Per batch
(c) Per unit (d) Per batch or unit
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 155