Page 203 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 203
Management Accounting
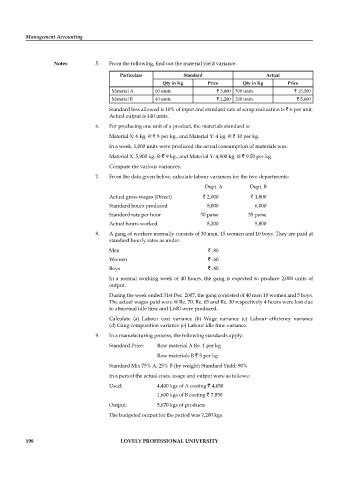
Notes 5. From the following, find out the material yield variance.
Particulars Standard Actual
Qty in Kg Price Qty in Kg Price
Material A 60 units ` 3,000 300 units ` 15,300
Material B 40 units ` 1,200 200 units ` 5,600
Standard loss allowed is 10% of input and standard rate of scrap realization is ` 6 per unit.
Actual output is 440 units.
6. For producing one unit of a product, the materials standard is:
Material X: 6 kg. @ ` 8 per kg., and Material Y: 4 kg. @ ` 10 per kg.
In a week, 1,000 units were produced the actual consumption of materials was:
Material X: 5,900 kg. @ ` 9 kg., and Material Y: 4,800 kg. @ ` 9.50 per kg.
Compute the various variances.
7. From the data given below, calculate labour variances for the two departments:
Dept. A Dept. B
Actual gross wages (Direct) ` 2,000 ` 1,800
Standard hours produced 8,000 6,000
Standard rate per hour 30 paise 35 paise
Actual hours worked 8,200 5,800
8. A gang of workers normally consists of 30 men, 15 women and 10 boys. They are paid at
standard hourly rates as under:
Men ` .80
Women ` .60
Boys ` .40
In a normal working week of 40 hours, the gang is expected to produce 2,000 units of
output.
During the week ended 31st Dec. 2007, the gang consisted of 40 men 10 women and 5 boys.
The actual wages paid were @ Re. 70, Re. 65 and Re. 30 respectively 4 hours were lost due
to abnormal idle time and 1,600 were produced.
Calculate (a) Labour cost variance (b) Wage variance (c) Labour effi ciency variance
(d) Gang composition variance (e) Labour idle time variance.
9. In a manufacturing process, the following standards apply:
Standard Price: Raw material A Re. 1 per kg
Raw materials B ` 5 per kg
Standard Mix 75% A; 25% B (by weight) Standard Yield: 90%
In a period the actual costs, usage and output were as follows:
Used: 4,400 kgs of A costing ` 4,650
1,600 kgs of B costing ` 7,850
Output: 5,670 kgs of products
The budgeted output for the period was 7,200 kgs.
198 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY