Page 235 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 235
Management Accounting
Notes
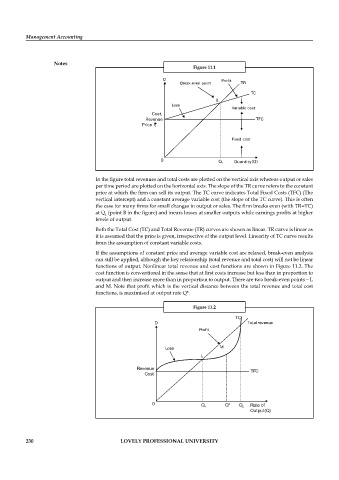
Figure 11.1
`
In the figure total revenues and total costs are plotted on the vertical axis whereas output or sales
per time period are plotted on the horizontal axis. The slope of the TR curve refers to the constant
price at which the firm can sell its output. The TC curve indicates Total Fixed Costs (TFC) (The
vertical intercept) and a constant average variable cost (the slope of the TC curve). This is often
the case for many firms for small changes in output or sales. The firm breaks even (with TR=TC)
at Q (point B in the fi gure) and incurs losses at smaller outputs while earnings profi ts at higher
1
levels of output.
Both the Total Cost (TC) and Total Revenue (TR) curves are shown as linear. TR curve is linear as
it is assumed that the price is given, irrespective of the output level. Linearity of TC curve results
from the assumption of constant variable costs.
If the assumptions of constant price and average variable cost are relaxed, break-even analysis
can still be applied, although the key relationship (total revenue and total cost) will not be linear
functions of output. Nonlinear total revenue and cost functions are shown in Figure 11.2. The
cost function is conventional in the sense that at first costs increase but less than in proportion to
output and then increase more than in proportion to output. There are two break-even points – L
and M. Note that profit which is the vertical distance between the total revenue and total cost
functions, is maximised at output rate Q*.
Figure 11.2
TC
D Total revenue
Profit
Loss M
L
Revenue
TFC
Cost
0 Q* Rate of
Q 1 Q 2
Output(Q)
230 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY