Page 25 - DMGT405_FINANCIAL%20MANAGEMENT
P. 25
Unit 2: Time Value of Money
Interest for second quarter ( 1015 × 0.06 × 1 × 1/4) 15.23 Notes
Amount available at end of second quarter 1030.23
Interest for third quarter ( 1030.23 × 0.06 × 1 × 1/4) 15.45
Amount available at end of third quarter 1045.68
Interest for fourth quarter ( 1045.68 × 0.06 × 1 × 1/4) 15.69
Amount available at end of first year 1061.37
With quarterly compounding, the initial investment of 1000 earned 1.37 more interest in the
first year than with annual compounding. Compound interest is defined with the following
terms:
P = principal sum earns
i = interest rate per period
n = number of period during which compounding takes place – a period can be
any length in time
Future Value of 1
A sum of money invested today at compound interest accumulates to a larger sum called the
amount or future value. The future value of 1000 invested at 6% compounded annually for
2 years is 1123.60. The future value includes the original principal and the accumulated interest.
Notes The future value varies with the interest rate, the compounding frequency and the
number of periods.
If the future value of 1 principal investment is known, we can use it to calculate the future value
of any amount invested. For example, at 8% interest per period, 1 accumulates as follows:
Future value of 1 at 8% for 1 period = 1.00000 × 1.08 = 1.08000
Future value of 1 at 8% for 2 periods = 1.08000 × 1.08 = 1.16640
Future value of 1 at 8% for 3 periods = 1.16640 × 1.08 = 1.25971
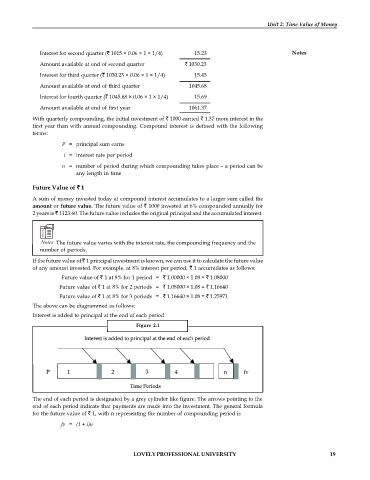
The above can be diagrammed as follows:
Interest is added to principal at the end of each period
Figure 2.1
The end of each period is designated by a grey cylinder like figure. The arrows pointing to the
end of each period indicate that payments are made into the investment. The general formula
for the future value of 1, with n representing the number of compounding period is
fv = (1 + i)n
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 19